STMicroelectronics along with the audio company USound has created the first MEMS (Micro ElectroMechnical Systems) micro-loudspeaker based on semiconductors. It’s the smallest loudspeaker in the world, but it can produce a powerful noise. MEMS makes it possible. The speakers are being presented at CES 2018 in Las Vegas.
In the audio world, the electromechanical capabilities of MEMS have only been used to build tiny microphones. Speakers, on the other hand, still rely on traditional dynamic design principles. It has taken almost 150 years for semiconductor technology to replace Werner von Siemens’ superior loudspeaker principle in 1877 with something newer. The Coil-magnet combinations are still being used in smartphones, wearables, and headphones to produce sound.
We can understand the working principle of MEMS speaker very briefly here. At first, thin piezoelectric layers are applied to a semiconductor(Silicon). An electric signal is sent to the piezoelectric layer allowing the diaphragm connected to it vibrate. Eventually, the mechanical principle resembles that of a normal Coil-magnet loudspeaker. The sound is created by the vibration in the diaphragm. However, the magnet and coil are replaced by a piezo element. By applying this new technique, USound’s MEMS version appears to offer significant advantages when it comes to distortion and THD or Total Harmonic Distortion.
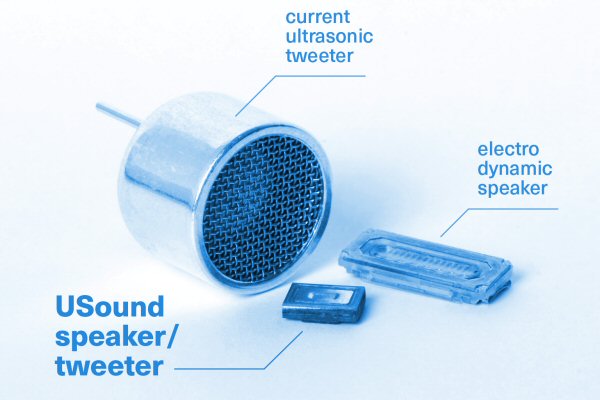
The MEMS loudspeaker developed by USound has dimensions of just 5 x 7 x 2 mm and has a frequency range of 2 to 15 kHz. It takes up half the space of its predecessors and needs only 20 percent of the energy that they do. The above figures are convincing enough for the speaker to be a perfect fit for mobile applications such as wearables and smartphones.
According to the manufacturer, these tiny speakers are the thinnest in the world. It has less than half the weight of a conventional Coil-magnet speaker. Most suitable applications include in many portable devices such as headphones, over-the-ear earphones, and more. With the help of this new speakers, augmented reality headsets or virtual reality systems can be more compact and comfortable. Innovative features also enable 3D sound production with striking accuracy. Its high efficiency reduces energy consumption and can easily be operated with much smaller and lightweight batteries. Higher efficiency results in less heat generated making systems operate cooler than ever before.