Debugging is an important part of the design process that is necessary to identify and fix errors. Over the decades, debug tools had evolved providing easier and simpler solutions. Today, ARM introduces CoreSight SoC-600 as the next-generation debug and trace tool that speeds up finding the root of the problem, with less iterations and lower risks.
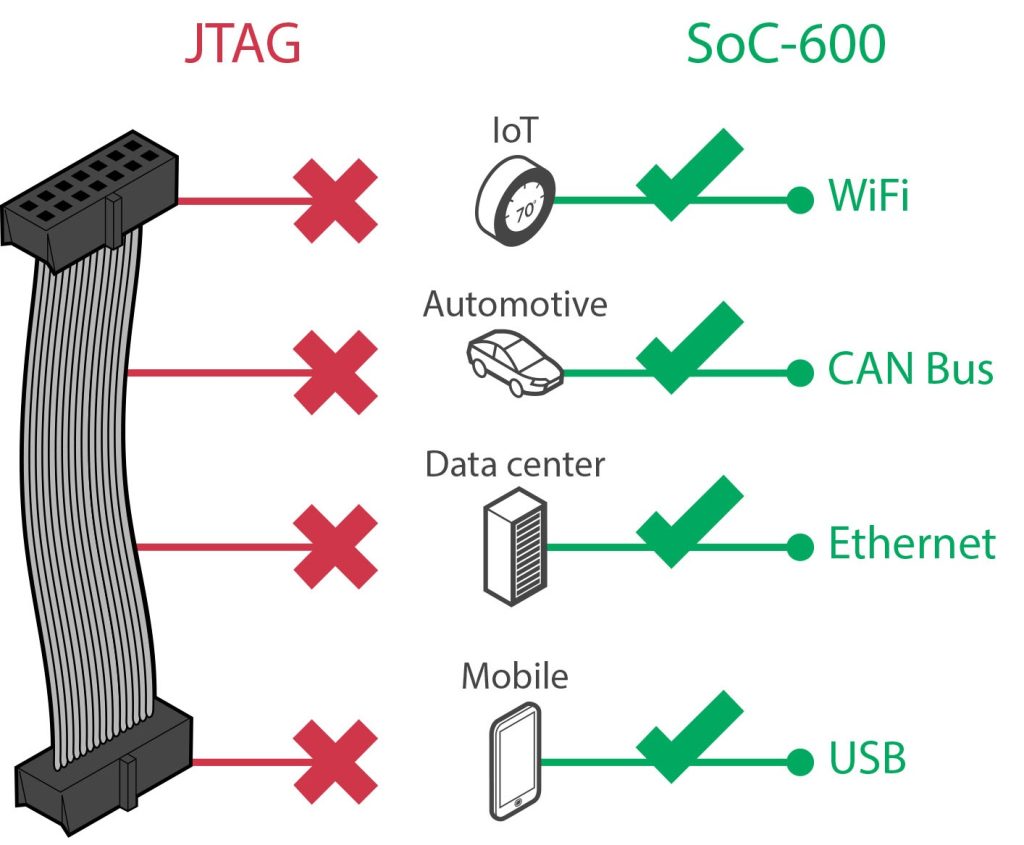
Addressing the requirements of the increasingly connected world characterized by faster product-development cycles, this new technology offers debug and trace over functional interfaces such as USB, PCIe or wireless, reducing the need for hardware debug probes while increasing data throughput.
Key benefits include:
- Debug access available and accessible throughout the product lifecycle, from production and manufacture, to remote access in the field
- Remote debug access (e.g. via Ethernet or wirelessly)
- Increased data bandwidth for improved system visibility
- Multiple debug agents can simultaneously access debug memory space (e.g. for concurrent external and self-hosted access)
- Interface peripherals (such as USB and PCIe) share a common access to APs, together with any existing JTAG DP or resident software
- Self-hosted, cross CPU debug access
CoreSight SoC-600 comes with a new Debug Access Port (DAP) architecture. It introduces standard APB connectivity between Debug Port (DP) and Access Port (AP), making it possible to have multiple DPs connected to multiple APs.
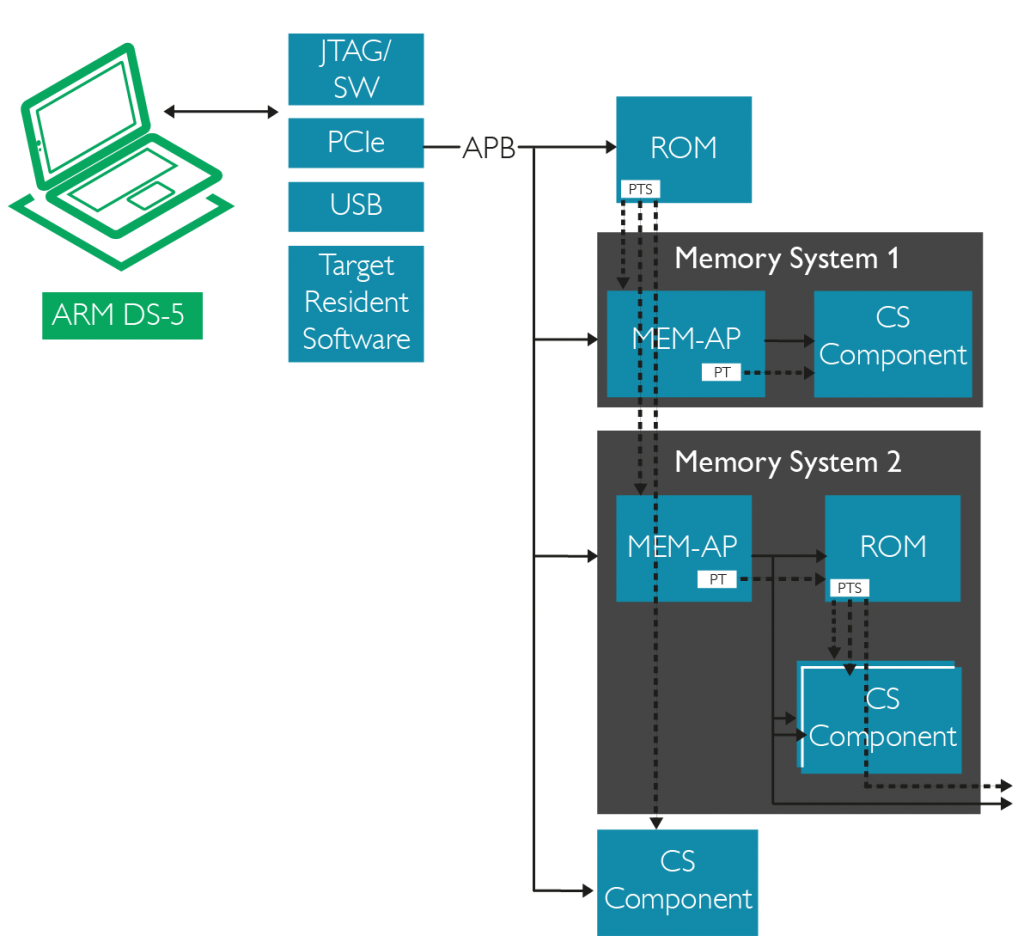
CoreSight SoC-600 also includes an enhanced Embedded Trace Router (ETR) functionality. In additional to removing the need for a separate Trace Memory Controller (TMC) license, enhancements to the Embedded Trace Router (ETR) configuration make it possible to supply a trace interface with four times the amount of bandwidth previously possible.
There are two approaches to host the link protocol when building a CoreSight SoC-600-based system:
- Protocol on dedicated CPU: this approach comes at a cost of additional dedicated resources, however, it is the least intrusive approach and provides bare metal debug capabilities.
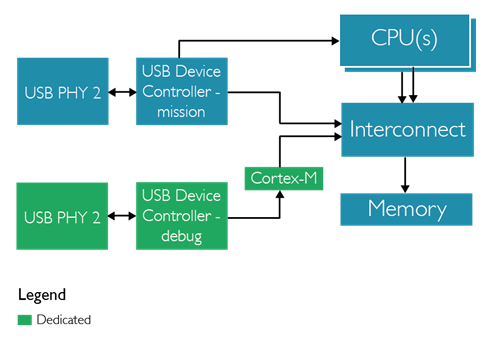
- Protocol on main CPU: this approach does not require additional hardware, yet it is invasive and relies on CPU not being halted.
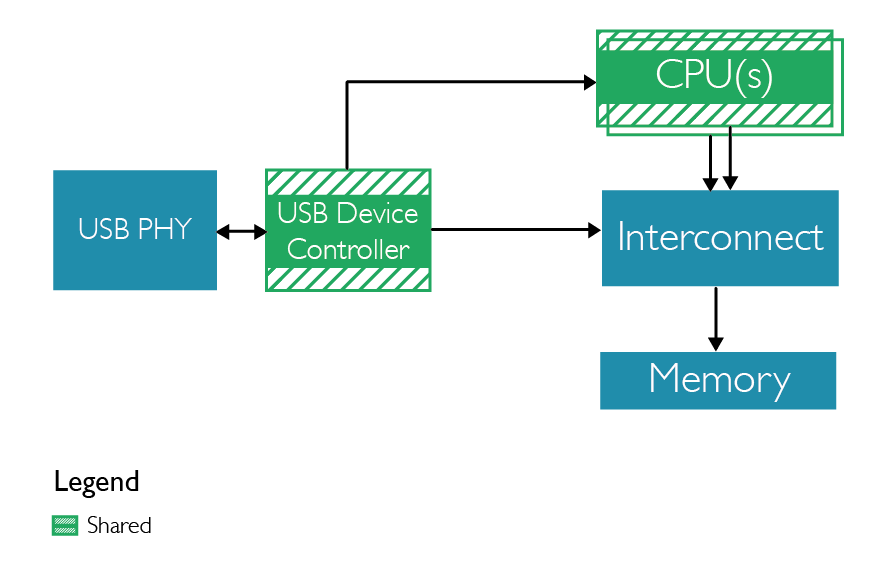
For further information and details about SoC-600 you can visit the official page, and the official article on ARM website.