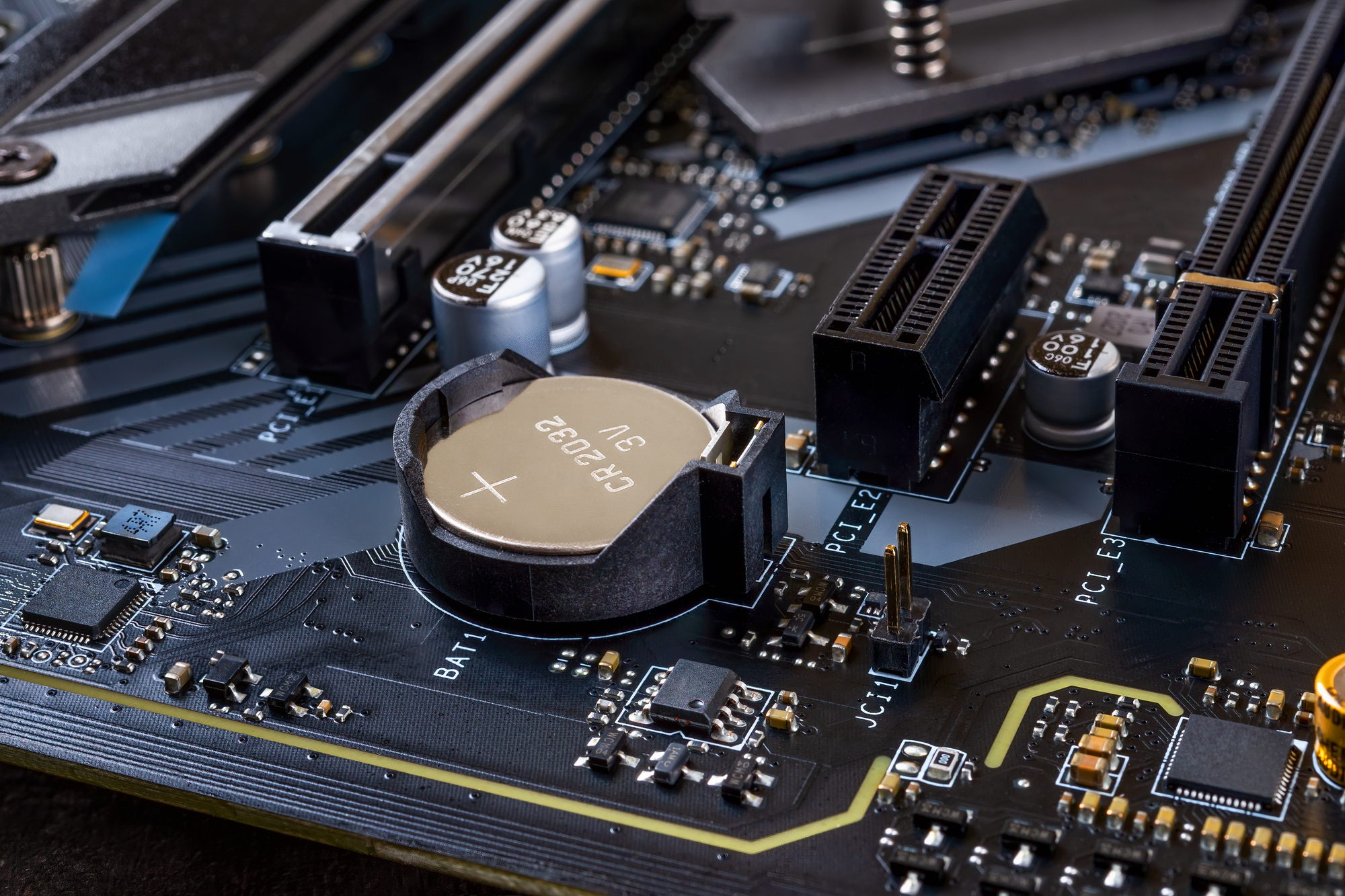
All motherboards are equipped with a CMOS battery. In the past, it was necessary to maintain the operation of the CMOS memory, which was responsible for storing BIOS data and other parameters of a personal computer. Previously, BIOS settings were stored in CMOS memory which was powered by an independent power source like batteries. With the advent of non-volatile memory, the need for the battery charge disappeared. But why do motherboards still come with CMOS batteries?
What does the CMOS battery do?
Just like regular watches need batteries to constantly maintain time, the computer’s internal clock also needs a constant power source. In addition, many older laptops use CMOS batteries to power the memory chip, which stores configuration settings like boot priority from a specific media, power saving mode, memory status, display type, keyboard settings, and other settings.
Like all other batteries, CMOS batteries also discharge over time. The average battery life is 5-7 years, but this value may vary depending on the manufacturer of a particular battery, battery capacity, and the operating environment of the computer.
How to tell if the battery on the motherboard is dead?
There are several signs by which you can easily determine that there is no power or if your battery will run out of power soon. Different laptops may have different symptoms and this is based on the manufacturer’s diagnostics protocol. Here are the most common signs of a dead motherboard battery:
- The first sign that indicates no power is a constant reset of the time and date. The BIOS is responsible for maintaining time, and the value is stored on a special chip on the motherboard. This micro-circuit is powered by a battery and therefore if there is not enough energy to power it, then the computer will reset the time and date during every boot cycle.
- The second sign is the constant reset of BIOS settings. The computer will reset the boot order and other settings.
- The third symptom is non-functioning apps. Some apps need to sync up with the server in the cloud to function and incorrect time won’t allow the sync to happen.
- Fourth sign. The computer won’t start at all. However, this mostly applies to older motherboards. Pay attention to the beeps or flashing LEDs that can be decoded through the factory service manual.
Where is the CMOS battery located?
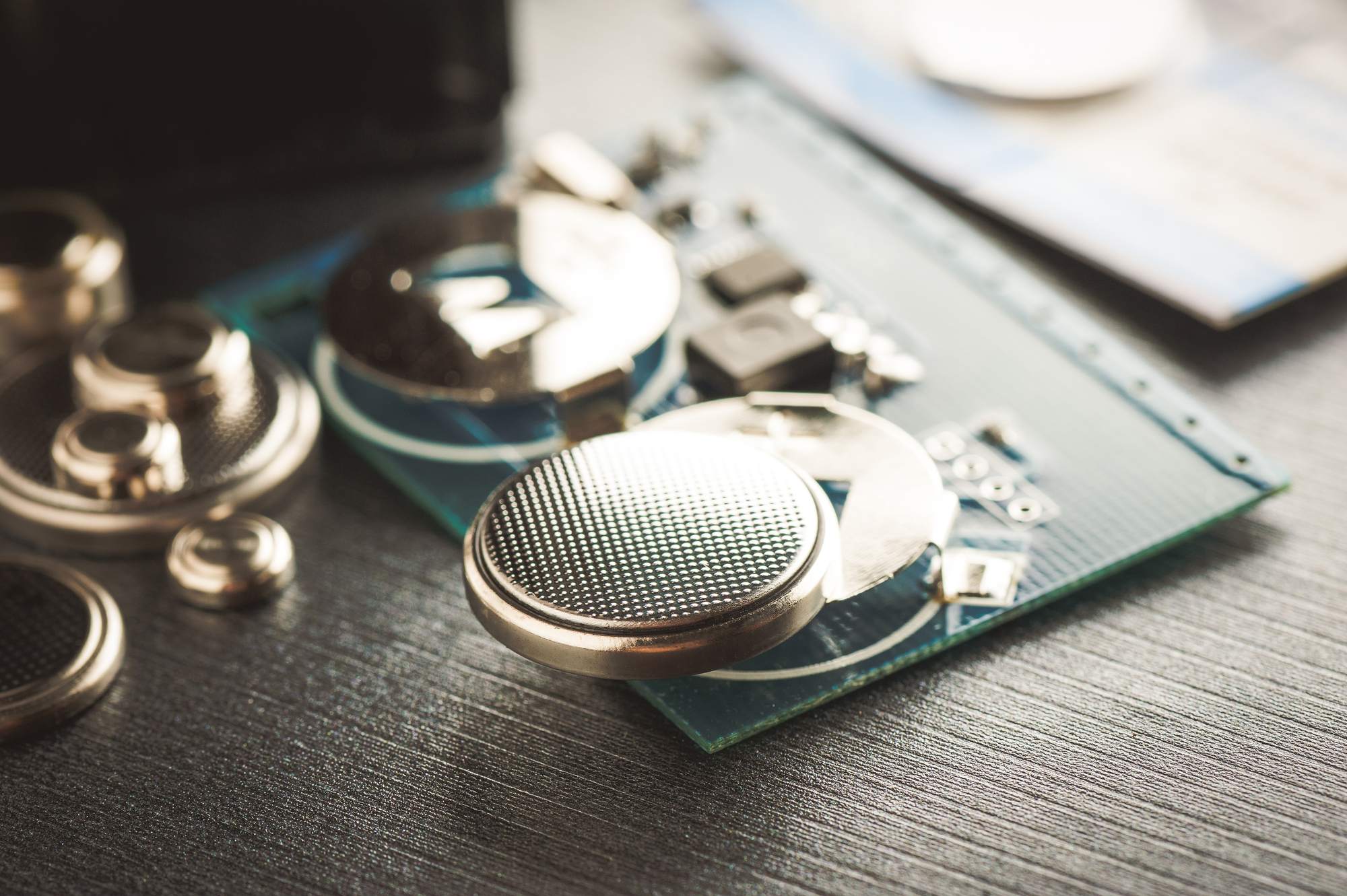
The location of the battery on the motherboard may vary depending on the manufacturer of the device, but it is almost always easy to visually identify it due to its shape and color. A typical coin-cell battery has a round shape with a diameter of around 2 cm and a metallic silver color. In some laptops, the battery is sealed inside an insulating protective film which can be black, yellow, blue, or any other color. The battery can be located near the CMOS chip or relocated to a different place on the motherboard via wires. On some boards, the battery may have a non-standard shape or multiple smaller batteries merged to form a bigger battery. Some batteries have a plastic holding container that is inserted or even soldered onto the board. In some laptop models, it can be very difficult for an ordinary user to get to the battery since it requires a complete disassembly of the device. A service manual can be checked beforehand to determine the location of the battery and the replacement procedure.
How to choose a CMOS battery?
Buying a new CMOS battery can be tricky because laptops use different connectors, voltage, polarity, wire length, and battery size.
Most laptops have a single-use CR2032 battery but on some occasions, smaller laptops use a rechargeable ML1220 battery. In addition to CR2032, some brands also use CR1220, CR1616, CR1620, CR1632, CR2016, CR2025, CR2450, and custom-made Ni-MH batteries. Sometimes battery type is not written on the battery shield, so the shield has to be carefully removed.
Connectors can also vary as some laptops have 2-pin and 3-pin of different shapes. Some 3-pin connectors use only two wires and have an unused pin. Wires are color-coded based on their polarity where red wire means positive and black or white wire means negative. It is important to pay attention to polarity to avoid damage to the motherboard.
Laptop motherboard design varies between each model and the CMOS battery slot is not always located near the connector. It is important to measure the length of the wires from the connector to the battery so the replacement battery can be located in the same slot as the original.
The typical battery voltage is 3V; however, some older custom Ni-MH batteries can go up to 7.2v. Generally, the original battery will have voltage and capacity written on it. The replacement battery has to have the same voltage to function correctly.
Motherboard battery removal and replacement
Before buying a new battery, remove your original battery and look for the part number. Buying a replacement with a matching part number guarantees a 100% fit. Most CMOS batteries are cross-compatible with different brands and some third-party manufacturers maintain a database of part numbers.
If your battery has no part number, then you can try to match it up visually with a replacement battery. You can find replacement pre-made batteries on Amazon and eBay, or through a specialized vendor like Rome Tech BIOS Batteries which can make a custom solution through their battery builder configurator. To use a configurator, you have to start by matching up the connector in step 1, polarity in step 2, cable length in step 3, and battery type in the last step.
Installation is very straightforward if a replacement battery is a 100% match. First, plug in the connector, then peel off the tape on the bottom and place it into the slot where the original battery was located. Your computer should boot up error-free and you will need to adjust the time and settings one last time.
[photos: www.depositphotos.com]