This RMS Voltage calculator helps to find the RMS voltage value from the known values of either peak voltage, peak-to-peak voltage or average voltage. It calculates the RMS voltage based on the given equations.
RMS (Root Mean Square) Voltage (Vrms)
Every waveform’s RMS value is the DC-equivalent voltage. Let’s take an example, if the RMS value of a
sine wave is 10 volts then it means you can deliver the same amount of power via DC source of 10 volts. Do not confuse in between Average voltage and RMS voltage, as they not equal.
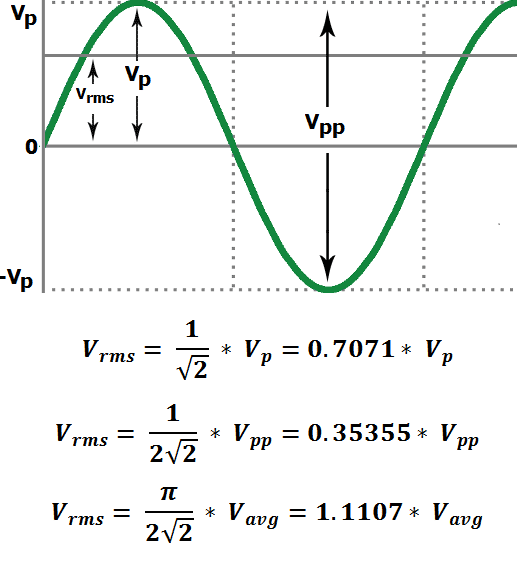
Peak Voltage (Vp)
A
Peak voltage of a sine wave is measured from the horizontal axis (which is taken from the reference point 0) to the crest (which is the top or maximum voltage level) of the waveform.
Peak voltage shows the
amplitude of the waveform.
Vp = √2 * Vrms
By, this formula we can get the value V
rms of with respect to peak voltage.
Vrms = 0.7071 * Vp
Peak-to-Peak voltage (Vpp)
The difference between maximum peak voltage and minimum peak voltage, or the sum of the positive and negative magnitude of peaks is known as the
Peak-to-Peak voltage.
Vpp = 2√2 * Vrms
By, this formula we can get the value of V
rms with respect to peak-to-peak voltage.
Vrms = 0.35355 * Vpp
Average voltage (Vavg)
The average value of a sine wave is zero because the area covered by the positive half cycle is similar to the area of the negative half cycle, so these value cancel each other when the mean is taken. Then the average value is measured by the half cycle only, generally we take the positive half cycle part for measuring.
The average voltage defined as “the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time”.
Vavg = 2√2/π * Vrms
By, this formula we can get the value of V
rms with respect to peak-to-peak voltage.
Vrms = 1.1107 * Vavg




