Category: Basic Electronics
Thermal design: Get the heat out of the electronics
Paul Rako@ edn.com discuss about thermal design in electronics and how to design your board to dissipate it effectively. If you have high-powered LEDS, or a power supply, or are trying to control larger motors, you have to get a lot of heat out of your circuit boards. The classic way...
Continue Reading
Measuring the speed of light with electronics
The speed of light in vacuum is a well-known universal constant and is considered to be the nature's ultimate speed limit. No matter, energy, and information can travel faster than this speed. The speed of light has always been a topic of great interest and significance throughout...
Continue Reading
Basic Electronics – How to use a 555 Timer
Do you want to know how to use a 555 timer? Laura brings you more Back to School tips and tricks on using this integrated circuit. Basic Electronics - How to use a 555 Timer -...
Continue Reading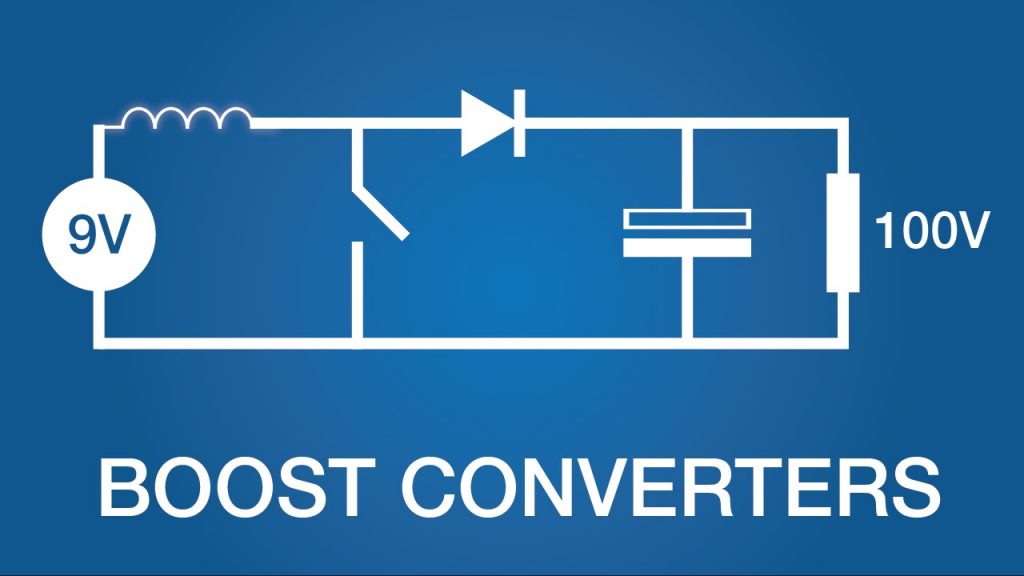
How Boost Converters (DC-DC Step-Up) Works
A look into how boost converters work in a very visual format. Try this circuit: http://goo.gl/nkHq9H How Boost Converters (DC-DC Step-Up) Works -...
Continue Reading
Zener Diodes In Theory and Practice
David Jones made a tutorial on the fundamentals of zener diodes over his EEVblog youtube channel. David started the tutorial comparing between zener and regular diode. Both have the same characteristics and same I-V chart, but zener is designed to work in the negative voltage...
Continue Reading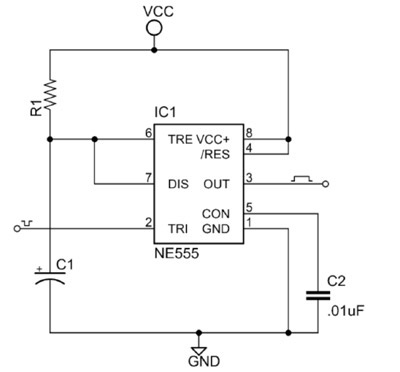
How To Configure a 555 Timer IC
Philip Kane @ jameco.com has published an article about the famous 555 timer IC and how to configure in monostable and astable modes. The 555 timer was introduced over 40 years ago. Due to its relative simplicity, ease of use and low cost it has been used in literally thousands of...
Continue Reading
What is a Zener Diode?
Let's have a look at what Zener Diodes are, and how they work! What is a Zener Diode? -...
Continue Reading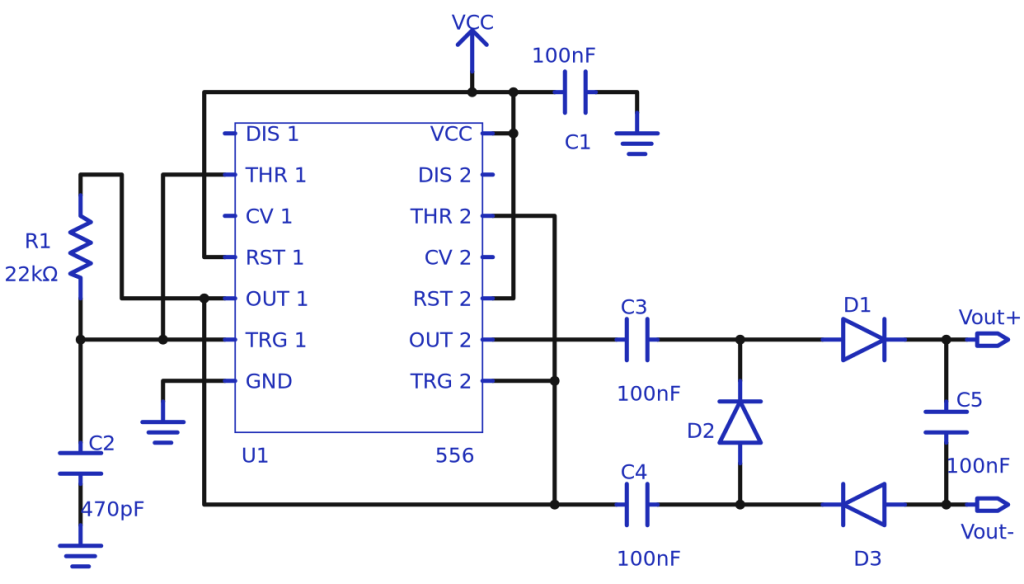
Charge-pump topology doubles voltage
Michael Dunn has designed a circuit that is able to double the input voltage and breaks DC path. I once needed a voltage doubler circuit with no DC leakage path between input and output, and ended up devising this unusual 556- (dual 555 timer) based circuit with a "floating" voltage...
Continue Reading