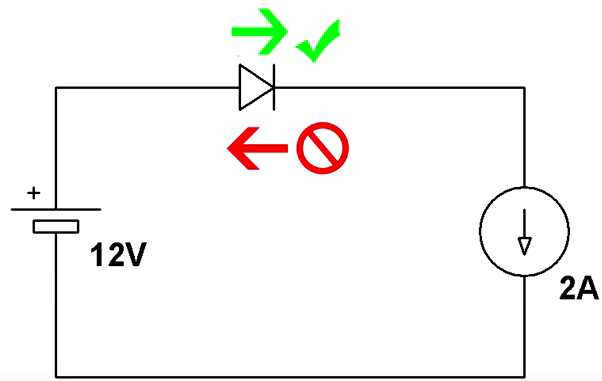
Diode or P-channel MOSFET is what you need to protect your circuit from applying reversed voltage, according to a nice video published on Afrotechmods channel.
Method 1:Diode
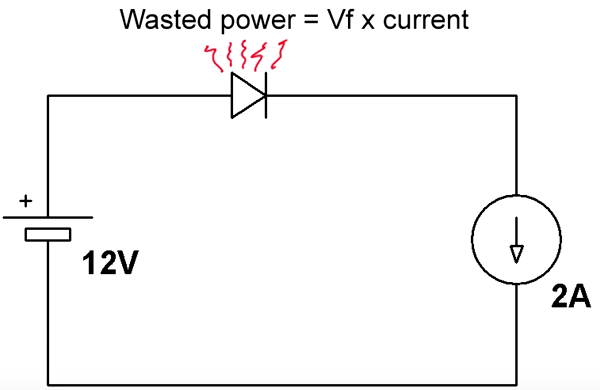
The simplest way is to use a diode in series with main power supply. When you connect the power source right, the diode anode is connected to positive side and the cathode will take the ground from the rest of the load which is connected to the ground.
The downside of using this method is the heat generated from the diode.
wasted power=Vf*current
So if we use a normal diode like 1n4007 for 2A:
wasted power=0.85*2=1.7W
If you connect the power source in reverse, then the diode will be off, thus protecting the circuit.
Method 1 (enhanced):Schottky Diode
In this way we can reduce the amount of power dissipated by the diode, as long Schottky Diode have a lower forward voltage compared with a normal diode.
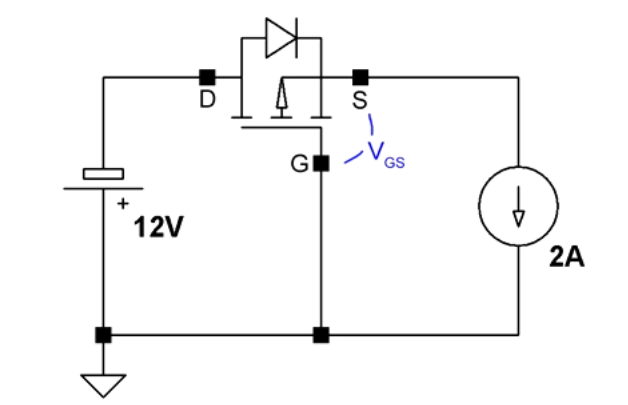
Method 2:P-channel MOSFET
You can use P-channel MOSFET like FQP47P0. In this method, when the power supply is connected properly, the Vgs is negative (you need to be above the threshold). When we power on the device, Vs is connected to Vd through the body diode of MOSFET and the MOSFET is on, the equivalent resistance between drain and source is very near to zero, for example Rds(on)=0.026ohm for FQP47P0.
wasted power=I*I*R=2*2*0.026=0.104W
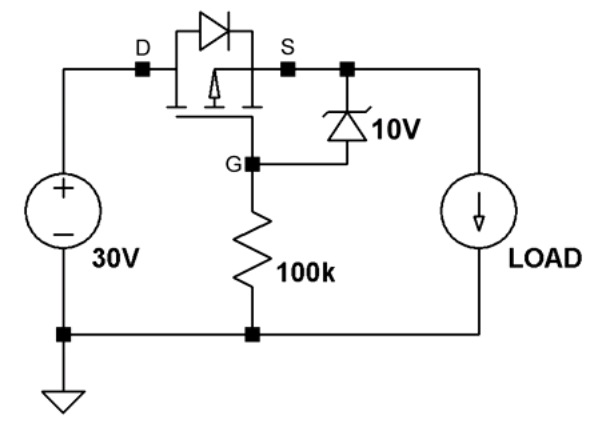
Method 2 (enhanced):P-channel MOSFET with Zener
In this method, we protect the MOSFET from applying Vgs with a limit that exceeds the breakdown voltage.