Everything You Need To Know About Bluetooth beacons in A White Paper
Bluetooth 4.0 introduced the Bluetooth low energy (BLE), which is a version of Bluetooth protocol designed for devices with power constraints like battery powered sensors. Bluetooth low energy beacons are BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) enabled devices, they repeatedly broadcast radio signals to nearby smartphones, containing a small amount of data.
Mobile apps can listen to the signals being broadcast and trigger an action after analyzing beacon’s information.
Beacons are used for proximity-aware applications like positioning and navigation indoors like anti-lost tracking tags, another application is for location based advertisements.
There is no official Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) beacon standard, so beacons have pseudo-standards. For example, iBeacon standard is used by Apple and Eddystone is used for Google.
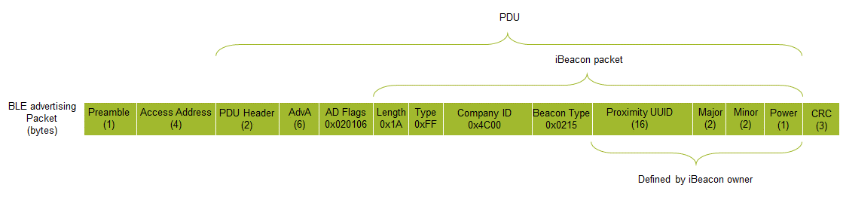
As you can see in the above image, there is one byte (power) value indicating the iBeacon’s calibrated output power in dBm measured at a distance of 1 meter.
So Beacons can be used to calculate the proximity distance between the beacon and the receiver of beacon’s information. This calculation relies on a comparison of a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) to a beacon’s transmit (Tx) power to approximate the distance to the beacon.
The calculated distance can’t be very accurate, since RF signals fade unpredictably according to real-world environmental factors like walls. Future versions of BLE will solve this by using Angle-of-Arrival (AoA) and Angle-of-Departure (AoD) which allow a multi-antenna Bluetooth device to accurately determine the spatial location of another Bluetooth device.
Beacons typically use non-connectable advertising, providing all of useful information in the advertising packet itself. So the radio can be shut off immediately after advertising hence this will save power.
A white paper from Silicon Labs covers a lot of informations about Beacons. The paper examines beacon applications, provides a short description of how BLE work, contains further description of iBeacon and Eddystone standards and highlights SoC solutions for BLE from Silicon Labs such as BLE112 and BLE113 which can have fully standalone applications through a simple scripting language called BGScript developed by Silicon Labs.
References:
Developing Beacons with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Technology
Beacons: Everything you need to know
Reading “Getting Started with Bluetooth Low Energy by Kevin Townsend, Carles Cufí, Akiba, and Robert Davidson (O’Reilly)” is advisable for anyone like to know more about who BLE works which is a corner stone to understand how beacons work.