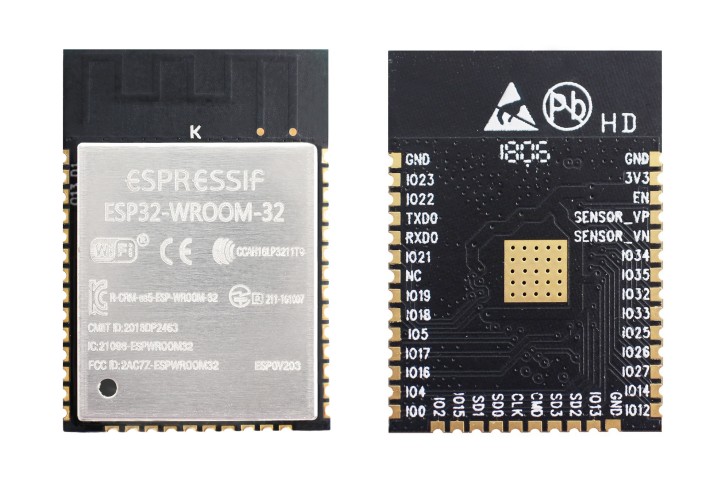
Over the last few articles, we have covered the use of ESP8266 boards for building several WiFi based projects. For today’s tutorial, we will look at it’s recently released successor; the ESP32.
As mentioned in previous tutorials, ESP-12e module popularly referred as the nodeMCU came at a time where makers were struggling with the difficulties around the use of the ESP-01 modules. The ESP-01 modules were not breadboard compatible, had power issues, and could barely be used in a standalone application where more than two GPIOs are required. The NodeMCU solved all these issues adding additional features and it immediately became a darling of the maker community. However, the ESP8266 equally had its own limitations and like every good product, there was a need to improve it. This improvement came in the form of the ESP32.
Getting Started with ESP32 – [Link]