New Energy-Harvesting Module Uses Electromagnetic Wave Noise from Common Devices to Provide Electrical Energy for IoT Sensors
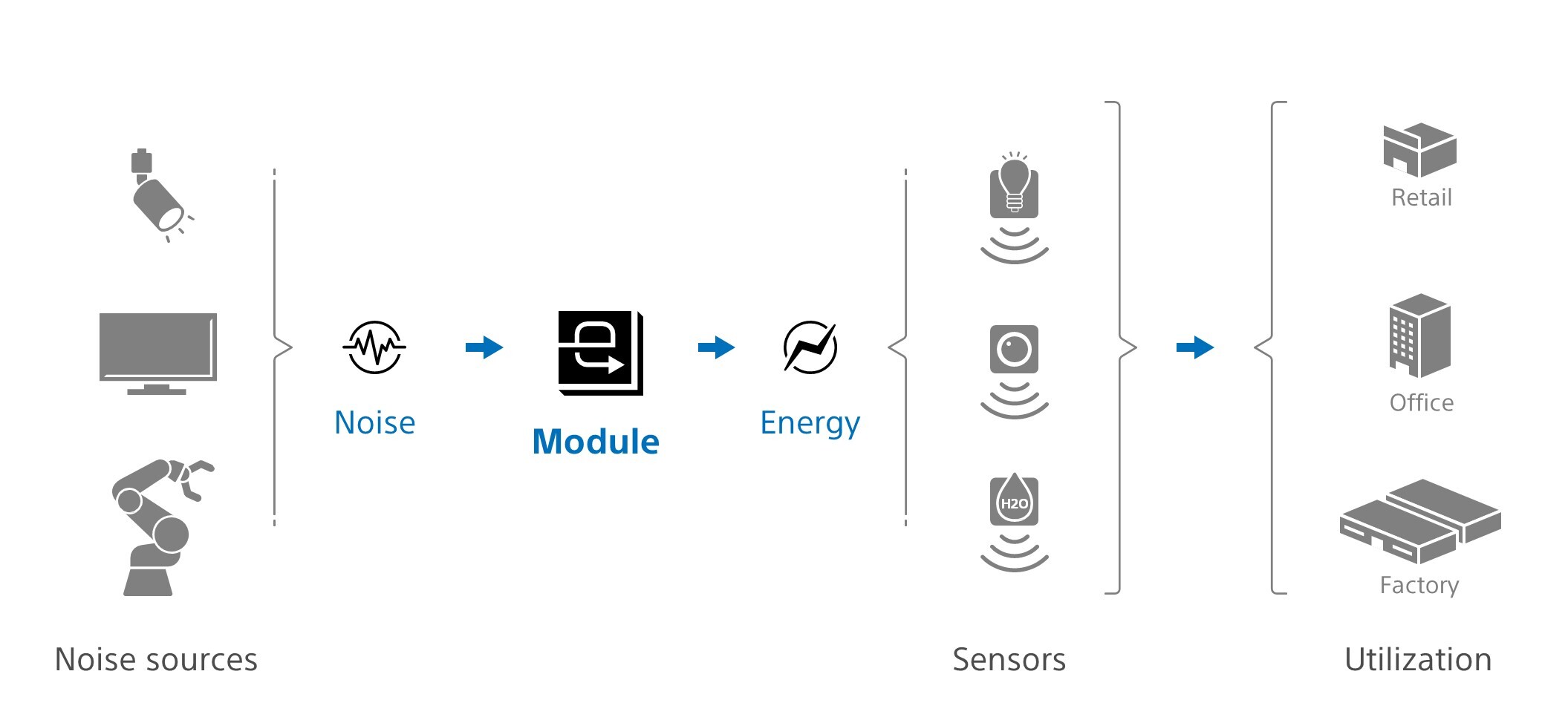
Sony Semiconductor Solutions has just developed a revolutionary energy-harvesting module that turns electromagnetic noise energy into usable power for sensors – a breakthrough in sustainable power supply technology intended to help resolve power supply issues arising from embedded devices. This method of power harvesting has a high level of power generation and it is applicable to a wide range of use cases including detecting the working status of electronic devices.
“The new module applies technology that SSS has cultivated in the tuner development process to generate power from electromagnetic wave noise with a high level of efficiency,” says Sony. “For example, this technology can use the constant electromagnetic wave noise generated by robots inside factories, monitors and lighting in offices, monitors and TVs in stores, homes, and the likes to provide the stable power supply needed to run low-power consumption IoT sensors and communications equipment.”
Other known energy harvesting systems harness sources ranging from solar energy to movement energy but this module chose to utilize electromagnetic noise instead. It uses a device’s existing metal parts as part of a receiving antenna for a high-efficiency rectifier circuit which can capture electromagnetic noise at different frequency levels, thus outputting milliwatt-level power for receiving sensors.
Key Points to Note About Sony’s Energy-Harvesting Module
- High level of generation and supply: It has the potential to harvest from several dozen μW to several dozen mW of Power, thus enabling it to supply power to low-power consumption sensors and equipment.
- Several Sources of Power Available: It can leverage electronic equipment as an energy source to generate a sufficient amount of electromagnetic wave noise. These equipment include household appliances, vending machines, industrial equipment, computers, lighting equipment, elevators, etc.
- Its method of harvesting power is not susceptible to environmental factors: Unlike other methods that rely heavily on factors such as indoor environments and lighting brightness, this method of power harvesting is only limited by the availability of power in the electronic devices. As long as electronic devices are powered, the module can always generate power from them.
- It enables continuous power harvesting: Even when the electronic devices are not in active use, the module can still harvest power from them.
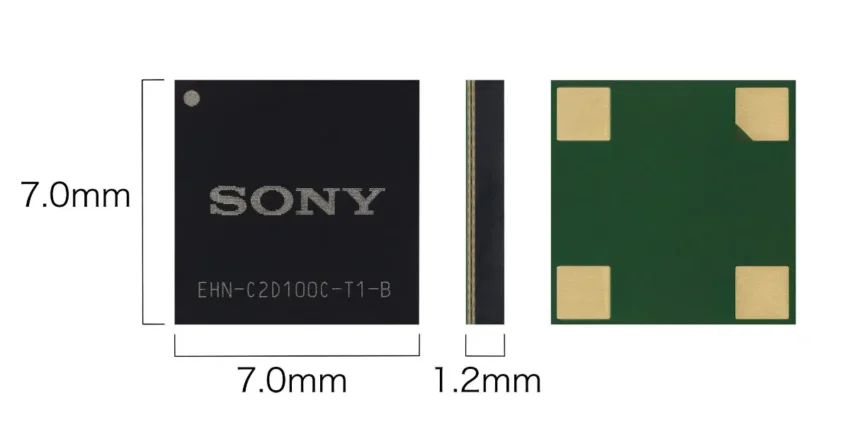
- It can easily be installed: The module has a compact size of 7mm by 7mm, hence allowing more freedom of installation.
- It can be used as a remote sensor for predictive maintenance in electronic devices: By observing the changes in the harvested voltage, the module can easily identify the internal status of the noise-generating device like detecting whether light is functioning normally or predicting device failure in devices with built-in motors.
Speaking on the future of this technology and what industries stand to gain from its adoption, the company claimed that the new innovation shows promise across a wide range of use cases and it plans to work with partners from various industries to develop products based on it.
“This is the industry’s first energy harvesting technology based on this method that achieves highly efficient power generation. By efficiently utilizing previously ignored electromagnetic wave noise as a new power source, it enables a stable power supply for equipment,” they said.
Sony’s energy-harvesting module is not ready to be commercialized yet, but other useful details are available on their website.