Resistive random-access memory (RRAM or ReRAM) is a type of non-volatile (NV) random-access (RAM) computer memory that works by changing the resistance across a dielectric solid-state material often referred to as a memristor.
Fujitsu Semiconductor has just launched world’s largest density 4 Mbit ReRAM product for mass production: MB85AS4MT. Partnering with Panasonic Semiconductor Solutions, this chip came to life.
The MB85AS4MT is an SPI-interface ReRAM product that operates with a wide range of power supply voltage, from 1.65V to 3.6V. It features an extremely small average current in read operations of 0.2mA at a maximum operating frequency of 5MHz.
It is optimal for battery operated wearable devices and medical devices such as hearing aids, which require high density, low power consumption electronic components.
Main Specifications
- Memory Density (configuration): 4 Mbit (512K words x 8 bits)
- Interface: Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
- Operating power supply voltage: 1.65V – 3.6V
- Low power consumption:
- Read operating current: 0.2mA (at 5MHz)
- Write operating current: 1.3mA (during write cycle time)
- Standby current: 10µA
- Sleep current: 2µA
- Guaranteed write cycles: 1.2 million cycles
- Guaranteed read cycles: Unlimited
- Write cycle time (256 byte page): 16ms (with 100% data inversion)
- Data retention: 10 years (up to 85°C)
- Package: 209 mil 8-pin SOP
This figure shows the block diagram of the chip:
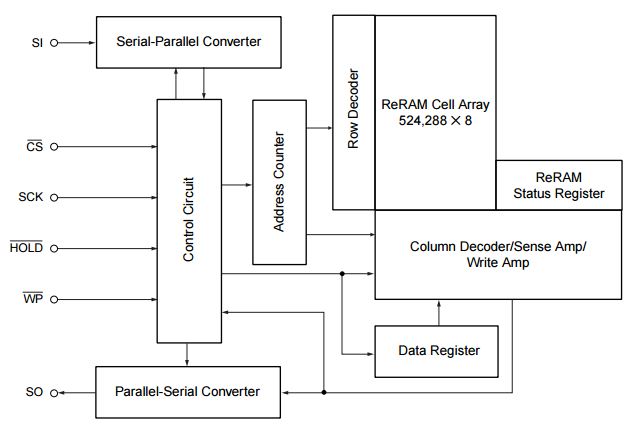
MB85AS4MT is suitable for lots of applications like medical devices, and IoT devices such as meters and sensors. In addition, the chip has the industry’s lowest power consumption for read operations in non-volatile memory.
For more information about MB85AS4MT, you can check the datasheet and the official website.