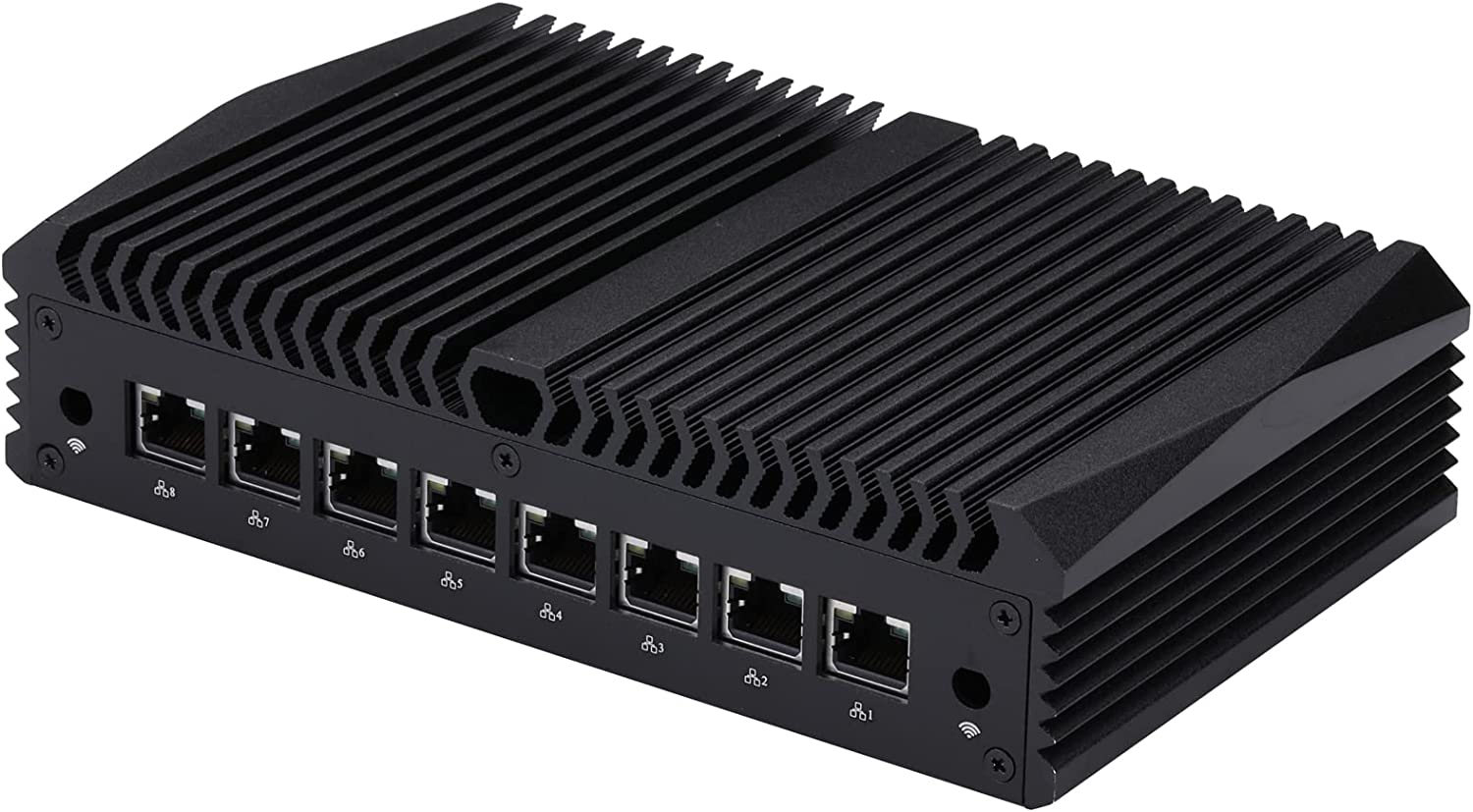
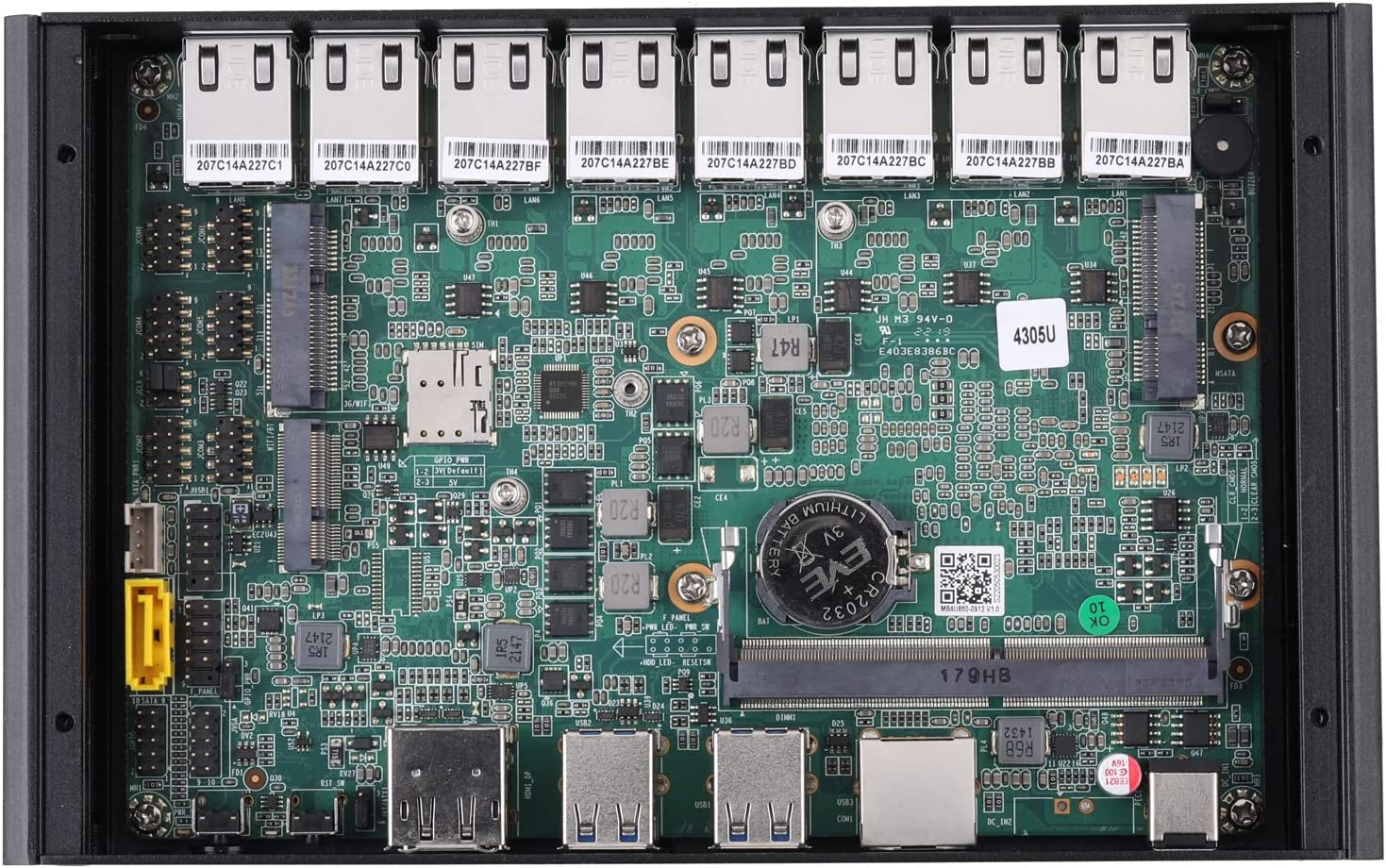
The InuoMicro G4305L8-S2 industrial PC box with eight 2.5GbE ports and a reasonably low cost is well suited for firewalls and other networking applications. It is powered by an Intel Celeron 4305U Whiskey Lake processor. The barebone computer offers interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort video outputs and a few USB ports, allowing the user to use it as a standard computer. It also supports up to 32 GB RAM, one mSATA SSD, and one 2.5-inch SATA drive. Using mini PCIe and/or M.2 4G LTE and WiFi modules, wireless connectivity can be implemented.
The InuoMicro G4305L8-S2 industrial PC box with eight 2.5GbE ports and a reasonably low cost is well suited for firewalls and other networking applications. It is powered by an Intel Celeron 4305U Whiskey Lake processor. The barebone computer offers interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort video outputs and a few USB ports, allowing the user to use it as a standard computer. It also supports up to 32 GB RAM, one mSATA SSD, and one 2.5-inch SATA drive. Using mini PCIe and/or M.2 4G LTE and WiFi modules, wireless connectivity can be implemented.
Advantages
It secures your network with a small, silent, fanless firewall that is more powerful than a typical router. A greater range of terminals is supported. Support for Linux iptables, Windows pfSense, Sophos, VyOS, Linux, Untangle, etc. Apply to affordable options for small office home office (SOHO) internet access, home labs, virtual offices, SMBs, branch offices, and locations for remote workers.

Specification:
- Products with an Intel Celeron Processor 4305U 2M Cache and 2.20 GHz Intel UHD Graphics for 8th Generation Intel Processors Whiskey Lake TDP 15 W.
- Item dimensions 8.66 inches long, 5.04 inches wide, 1.85 inches high, and 4.4 pounds.
- The operating temperature is between 0 and 50 degrees Celsius, and the non-operating temperature is between -20 and 80 degrees Celsius.
- The hard drive can also hold one Mini-PCIe for mSATA SSD and one 2.5 “SATA SSD/HDD. (2.5 “Included is a SATA cable)
- Memory up to 32 GB is supported by 1 x DDR4 SO-DIMM Socket, 2133/2400 MHz.
- It has one full-length Mini PCIe for 4G and one half-length Mini PCIe for Wi-Fi only. Help USB Devices and M.2 Wi-Fi (E key, 2230)
- 8 Intel I225V 2.5G LANs are used for the local area network.
- There is also one SIM card slot, one GPIO, one COMS Clear Jumper, and one Automatically Boot Jumper.
- Item size is about 220 x 128 x 47 mm.
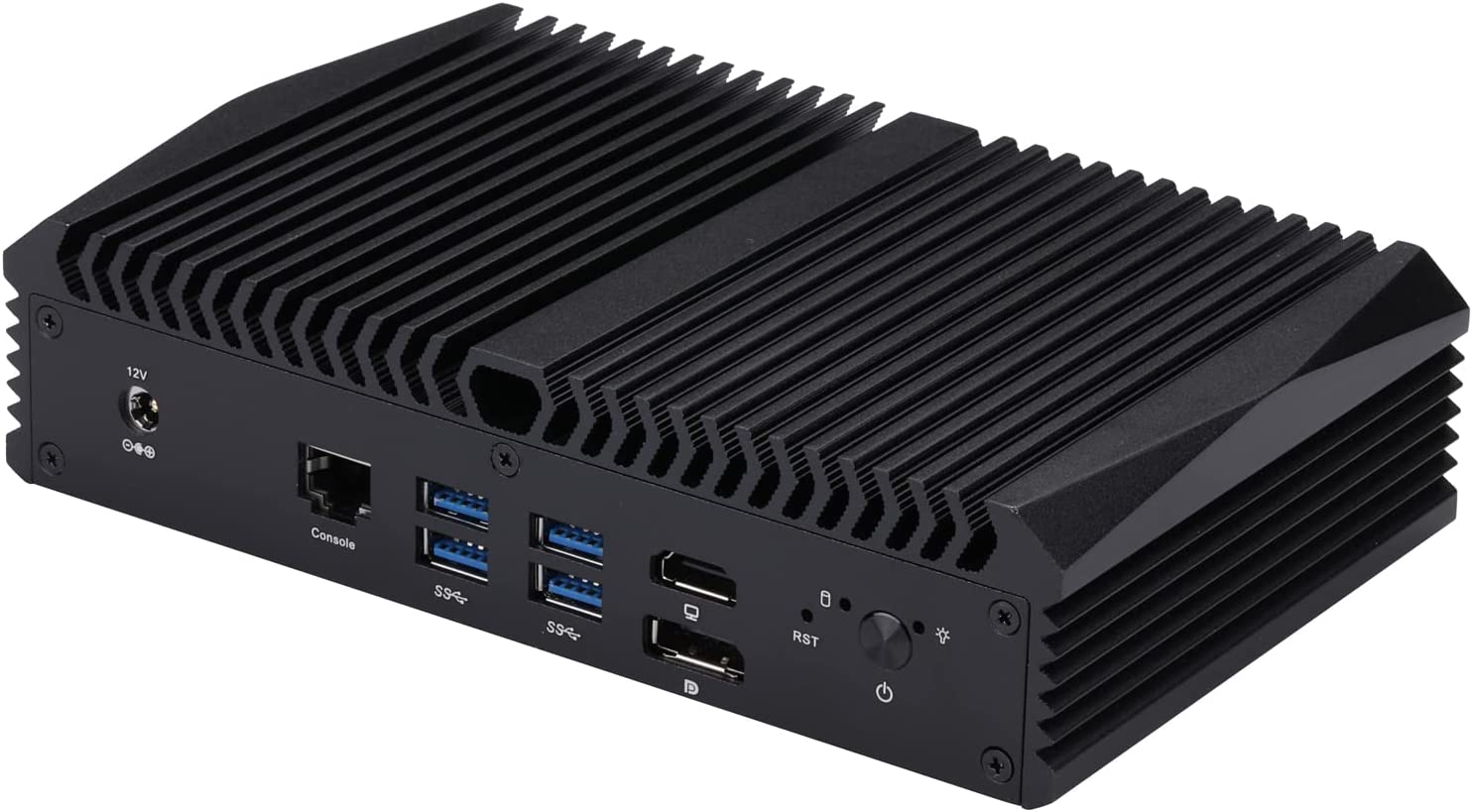
- Front I/O has 1 x Power on/off Button, 1 x Reset Button, 4 x USB 3.0, 2 x USB 2.0, 1 x DC Jack, 1 x 2*3.5 mm Connector, 1 x HD Video, 1 x DP port.
- There are 8 Intel I225V 2.5G LAN ports on the back I/O.
- It can act as a host and can be used at home, the office, the library, the hospital, a restaurant, a bank, and almost any other place where a computer is needed.
- Windows 10, Linux, Ubuntu, Pfsense, CentOS, and Untangle are all supported operating systems. The Intel Celeron 4305U is on the list of processors supported by Microsoft’s most recent operating system, but Windows 11 is not.
On Amazon, InuoMicro is offering the G4305L8-S2 box PC for a price of $203, and if it was simply an OEM model that would soon be sold under different brands, it would not be a surprise.