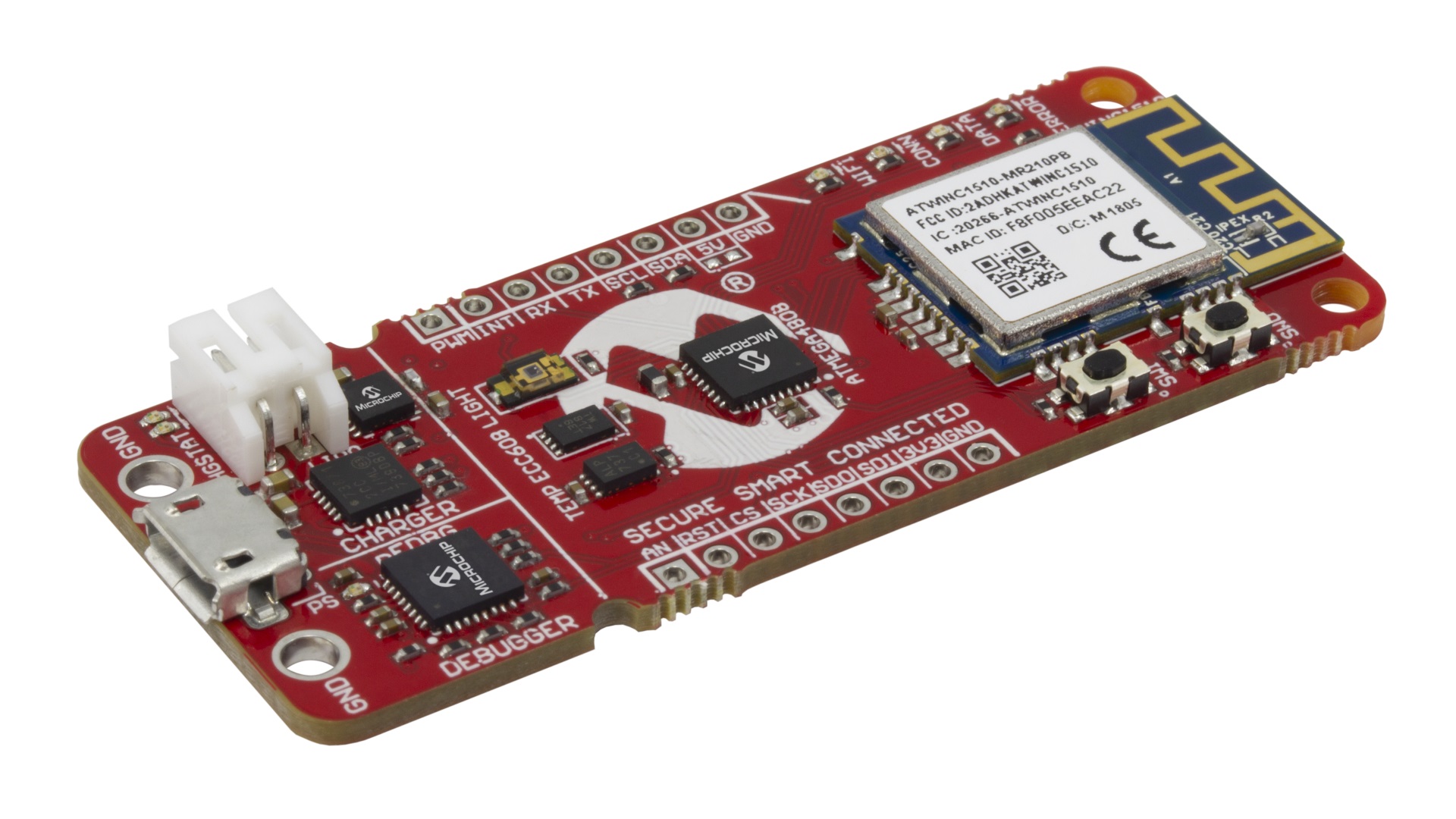
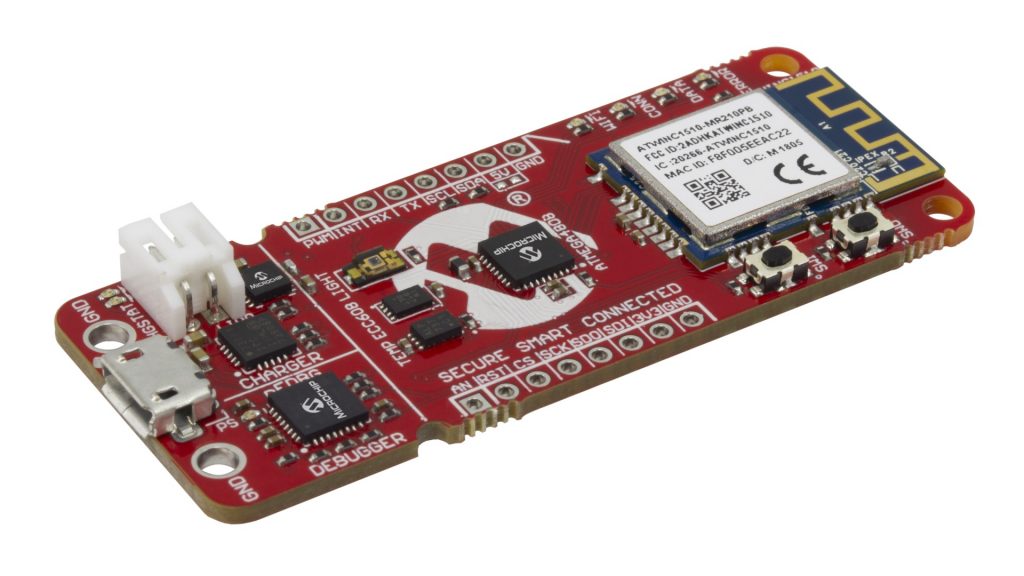
Microchip released a new IoT Development board, the AVR-IoT WG with part number: AC164160
The AVR-IoT WG development board combines a powerful 8-bit ATmega4808 MCU, an ATECC608A CryptoAuthentication™ secure element IC and the fully certified ATWINC1510 Wi-Fi® network controller – which provides the most simple and effective way to connect your embedded application to Google’s Cloud IoT core platform. The board also includes an on-board debugger, and requires no external hardware to program and debug the MCU.
Out of the box, the MCU comes preloaded with a firmware image that enables you to quickly connect and send data to the Google Cloud IoT platform using the on-board temperature and light sensors. Once you are ready to build your own custom design, you can easily generate code using the free software libraries in Atmel START or MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC).
The AVR-IoT board is supported by two award-winning Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) – Atmel Studio and Microchip MPLAB® X IDE – giving you the freedom to innovate with your environment of choice.
Smart – Expand IoT functionality using the powerful ATmega4808 with 48 KB Flash and 6 KB RAM.
Secure – Entrust encryption to the latest in Microchip’s CryptoAuthentication portfolio, based on ATECC608A.
Connected – Propel your design into the Cloud with Microchip’s ATWINC1510, a single-band 2.4 GHz network controller.
ATmega4808 microcontroller
- Four user LED’s
- Two mechanical buttons
- mikroBUS header footprint
- TEMT6000 Light sensor
- MCP9808 Temperature sensor
- ATECC608A CryptoAuthentication™ device
WINC1510 WiFi Module
On-board nEDBG Debugger
- Auto-ID for board identification in Atmel Studio and Microchip MPLAB X
- One green board power and status LED
- Programming and debugging
- Virtual COM port (CDC)
- Two DGI GPIO lines
USB and battery powered
Integrated Li-Ion/LiPo battery charger