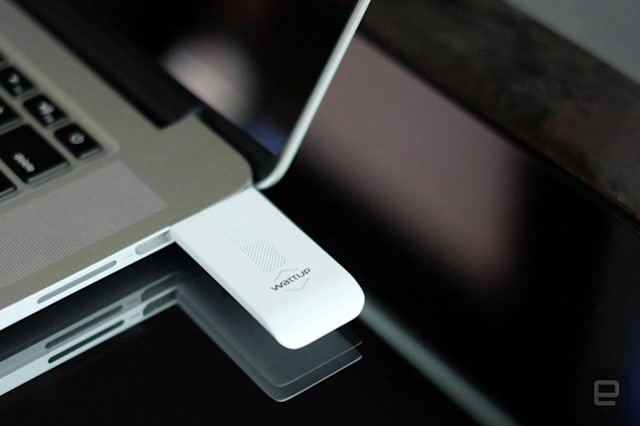
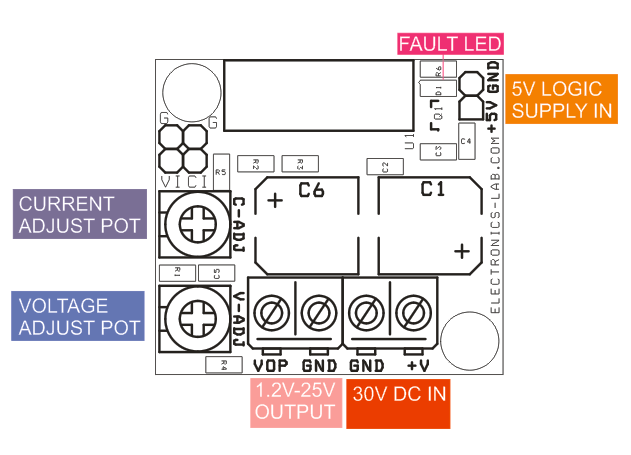
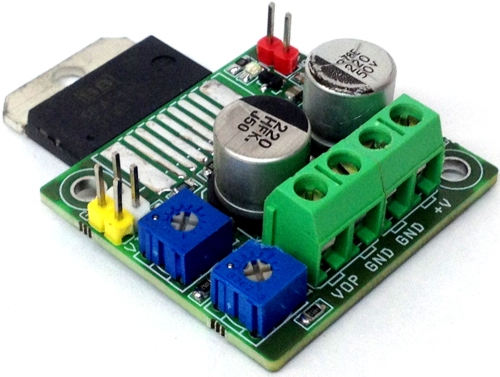
Automotive industry has noticed the growing trend of internet of things and used it as a business opportunity for connecting their cars. By 2020, 381 million cars are expected to be on the road. Even when you can buy a IOT car there are few or none customization opportunities which is what differentiates AutoPi from other systems. A group of software developers created a device called AutoPi dongle based on Raspberry Pi which allows the user to fully customize their car which could change the way you drive.
Autopi is built on RSA and AES encryption to ensure total security and efficiency. The infrastructure is based on SaltSack and the device is based on the Raspberry Pi. The AutoPi dongle has WIFI, GPS, Bluetooth, HDMI out, 3G/4G connectivity, USB, accelerometer and much more. Additionally, they created the AutoPi cloud which allows remote monitoring, alerts, triggers etc.
Any external device can be connected to the AutoPi dongle to achieve much more. Some projects that have already been implemented include crash detection, collision prevent assistant, theft detection, parental control and video evidence recording. With the GPS and the historic trip widget included in the software you can know where your car was at any time.
It’s a perfect device for young new drivers and their worried parents who want to keep track of their kid’s speed, use of seatbelt etc. using a variety of sensors, all this information could be accessed remotely. Also, during summer the is nothing worse than getting into a car that has been left out in the sun. Hot weather can also shorten your battery’s usable life, and it’s a hazard for pets left in the car. Heat monitoring can detect the temperature and lower the windows slightly to prevent the temperature from rising too high, or during winter the car could be heated before you arrive. You can trigger an internal system, an external system, and an externally connected system in order to bring your projects to life.
For 94,5 € you can get the DIY edition, for 189 € the WIFI only edition, and 4G for 247,5 €. In the webpage you can also get the Raspberry Pi 3 adapter. The price is still a bit too high for a car accessory, but when you think about the possibilities and the improvement in your car and your lifestyle it is not that expensive.
[source]