u-blox, a global provider of positioning and wireless communication technologies and services, has announced the u-blox ANT-B10 antenna board for Bluetooth direction finding and indoor positioning applications. Designed for integration into commercial end-products, the board enables low power, high precision indoor positioning and speeds up evaluation, testing, and commercialisation of Bluetooth direction finding and indoor positioning solutions.
Bluetooth indoor positioning uses the angle of arrival (AoA) of a Bluetooth direction finding signal emitted by a mobile tag at several fixed anchor points to calculate the tag’s location in real-time with sub-meter accuracy. The technology, which benefits from Bluetooth’s vast ecosystem and interoperability across platforms, is gaining traction due to its low cost, high accuracy, and relative ease of installation and maintenance.
Assembling an AoA indoor positioning anchor in seconds
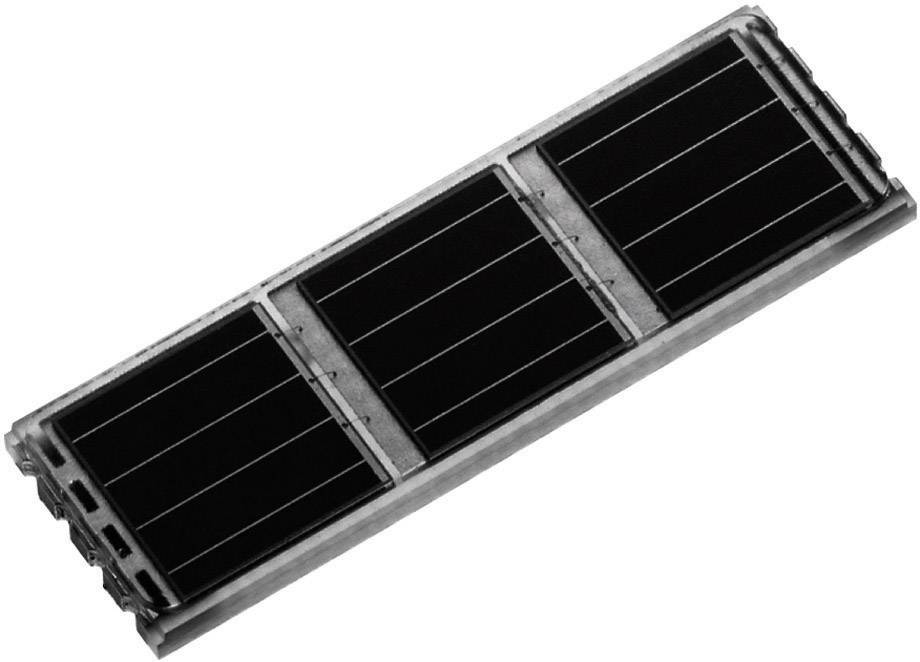
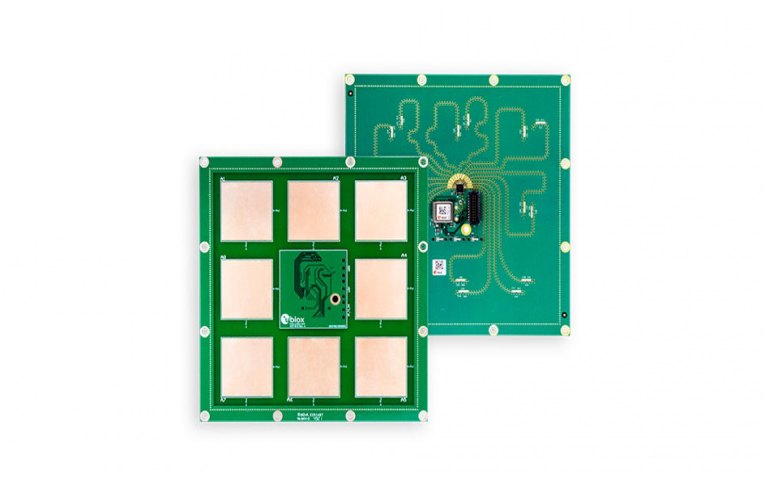
ANT-B10 is a self-contained Bluetooth low-energy antenna board for direction finding and indoor positioning. The board, which features an antenna array comprising eight individual patch antennas, is built around a u-blox NINA-B411 Bluetooth 5.1 module. After processing incoming RF signals emitted by mobile tracker tags in the module’s radio and angle calculation processor, the solution outputs the calculated angle of arrival without requiring any additional processes.
The release also includes the XPLR-AOA-3 explorer kit. It features an application board, which offers developers a quick and easy way to evaluate and test the ANT-B10 antenna board, as well as u-blox’s direction finding algorithm. An off-the-shelf pin header on the application board allows for easy bring-up and testing of ANT-B10 and third-party antenna boards. And connecting the two boards yields a ready-to-use AoA indoor positioning anchor point in seconds.
Ready to go for end-product integration
ANT-B10 and XPLR-AOA-3 complements the existing u-blox indoor positioning offering, which includes the popular XPLR-AOA-1 and XPLR-AOA-2 kits. Using u-connectLocate, which runs on ANT-B10’s Bluetooth module, solution developers can easily execute the angle calculation algorithms using AT commands. When combined, the solution suite is ready to go for end-product integration.
Common use cases for Bluetooth indoor positioning and direction include tracking assets in industrial settings such as in warehouses as well as people and things in hospitals, retail environments, or museums. Additionally, access control systems deployed in connected buildings can use angle detection to determine which side of a door users are located on.
Actively engaged with the technological ecosystem
To determine the angle of arrival of incoming signals for direction finding, the ANT-B10 board concurrently processes them on all eight patch antennas. Because implementing multiple RF paths connected to multiple RF switches unnecessarily increases power demand and introduces errors, the ANT-B10 board uses an industry-leading single RF switch component from u-blox partner CoreHW that cycles through the eight antennas at a microsecond timescale.
“We are excited to be part of such a great all-round indoor positioning solution. u-blox has really demonstrated its commitment to bringing down the barriers to entry for Bluetooth indoor positioning solutions and popularizing the technology,” says Mika Jäsberg, VP Components at CoreHW.
“With the introduction of ANT-B10 and the XPLR-AOA-3 kit, we are excited to offer a complete u-blox RF-to-cloud solution for Bluetooth-based indoor positioning and direction finding. The solution lets developers benefit from our in-house expertise in angle calculation and multipath suppression, saving development costs and shortening time to market,” says Giorgos Marakis, Product Strategy, Short Range Radio, at u-blox.
The ANT-B10 boards are available today – sampling of ANT-B10 to customers has already begun.