With the all-new R&S MXO 5, Rohde & Schwarz continues to evolve its series of next-generation oscilloscopes, started with the successful R&S MXO 4 in 2022. The R&S MXO 5 is the company’s first eight-channel oscilloscope. It expands upon the industry-firsts pioneered by the R&S MXO 4 and will empower engineers to tackle even more demanding design challenges.
Rohde & Schwarz presents its new R&S MXO 5 oscilloscopes, available with four or eight channels. Building on next-generation MXO-EP processing ASIC technology developed by Rohde & Schwarz and introduced with the R&S MXO 4, the new eight-channel R&S MXO 5 oscilloscopes take measurement performance to the next level.
Industry firsts in an eight-channel oscilloscope
The new R&S MXO 5 shows more of a signal’s activity in both the time and the frequency domains than any other oscilloscope. The R&S MXO 5 is the world’s first eight-channel oscilloscope with 4.5 million acquisitions per second and 18 million waveforms per second across multiple channels. Engineers can capture intricate signal details and infrequent events with exceptional precision. The R&S MXO 5 has digital triggering on all eight channels to surpass its competitors in the accurate isolation of small signal anomalies. The groundbreaking capability of 45,000 FFTs per second provides engineers with unparalleled spectrum signal viewing, particularly for EMI and harmonic testing.
By capturing up to 99% of real-time signal activity with the fastest acquisition capture rate in the world, the R&S MXO 5 speeds up signal analysis while detecting rare and random events missed by most other oscilloscopes. The features let engineers debug designs more efficiently across multiple applications – from power conversion to automotive analysis – making power and signal integrity measurements as well as logic and bus protocol debugging a breeze.
Philip Diegmann, Vice President of Oscilloscopes at Rohde & Schwarz, says:
“Launching the R&S MXO 4 in 2022 introduced the next generation of oscilloscopes with unmatched performance and value. At Rohde & Schwarz, we continue to evolve the usability of our oscilloscopes to new levels. Today, we are excited to introduce the R&S MXO 5, continuing our legacy of oscilloscope excellence. Building on the same engineering breakthroughs, this oscilloscope series was meticulously designed by our dedicated development team to capture both the big picture and smallest details of electrical signals with unparalleled accuracy and speed. Evolved for more challenges, the scopes will speed up our customers’ understanding and testing of their electronic systems.”
Deepest-in-class standard memory
The R&S MXO 5 series offers standard simultaneous acquisition memory of 500 Mpoints across all eight channels or double the standard memory of the competition. The ample storage can be used for extensive data capture. Furthermore, a memory extension option can double the recording length to 1 Gpoints for the most demanding applications. The exceptional memory depth in the R&S MXO 5 oscilloscope is critical for a wide range of troubleshooting tasks, enabling the capture of extended periods of time and retaining accurate bandwidth information even with slower time base settings.
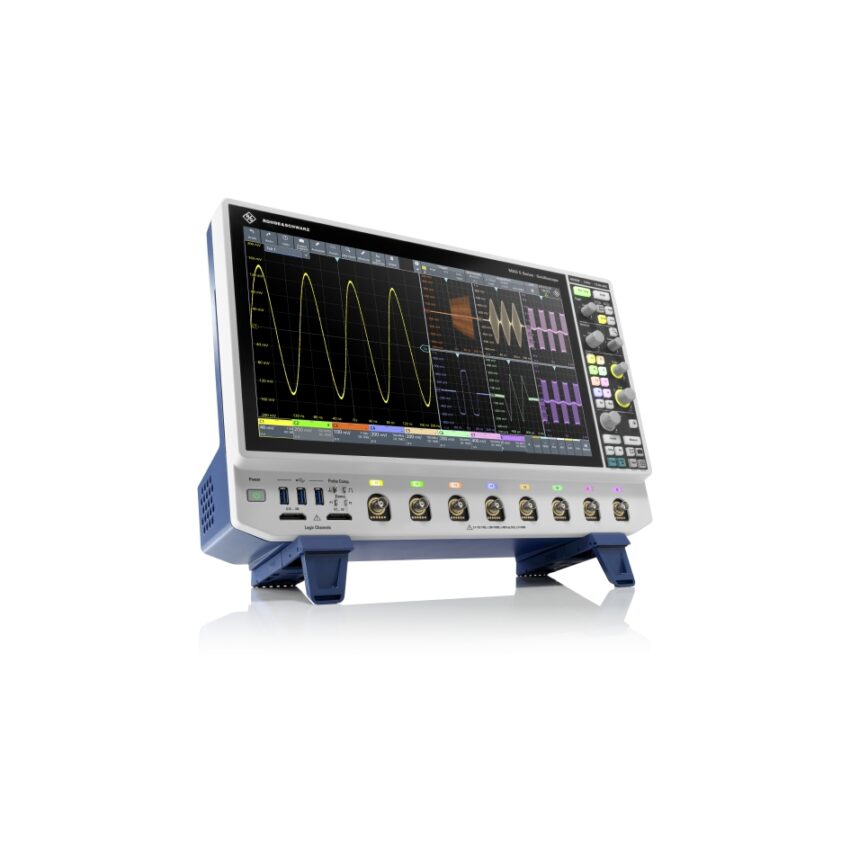

First digital trigger for eight channels
As the first eight-channel oscilloscope with digital triggering, the R&S MXO 5 sets a new standard in signal analysis. The digital trigger outperforms all other oscilloscope triggers with a remarkable sensitivity of 0.0001 div. The sensitivity helps precisely isolate small physical layer anomalies, even when large signals are present. No other instrument on the market can match this trigger sensitivity. Other instruments often require signal processing corrections to align analog path trigger events, resulting in a slower and noisier trigger performance. The digital trigger seamlessly complements the 18-bit vertical architecture in the oscilloscopes, so that engineers can fully leverage the precision of the R&S MXO 5.
Superior RF measurement
The R&S MXO 5 excels in RF measurements, both in the time and frequency domains. It is the first oscilloscope with 45 000 FFTs (Fast Fourier Transforms) per second. The exceptional speed, combined with the ability to display four different time-independent spectra simultaneously provides engineers with outstanding RF signal visibility unmatched in its class. The advanced capabilities are standard R&S MXO 5 features.
Evolved user experience
An unparalleled large 15.6″ full-HD capacitive touchscreen and an intuitive user interface optimize the learning curve and give R&S MXO 5 oscilloscopes a seamless and engaging visual experience. The small footprint and first-in-class VESA mounting make the oscilloscopes ideal for any engineering workspace. The R&S MXO 5 has industry’s lowest audible noise level that is quieter than a whisper for a focused lab environment where engineers can perform their tasks precisely.
Low starting price
The R&S MXO 5 oscilloscopes are available in four and eight-channel models, in bandwidth ranges with 100 MHz, 200 MHz, 350 MHz, 500 MHz, 1 GHz, and 2 GHz models. The eight-channel models start as low as EUR 19 500, the industry’s lowest entry price in this instrument class. Various upgrade options are available to users with demanding application needs, such as 16 digital channels with a mixed-signal oscilloscope (MSO) option, an integrated dual-channel 100 MHz arbitrary generator, protocol decode and triggering options for industry-standard buses and a frequency response analyzer to enhance the capabilities of the instrument.
The new R&S MXO 5 series oscilloscopes are now available from Rohde & Schwarz and selected distribution channel partners. Rohde & Schwarz will demonstrate the new R&S MXO 5 at Productronica 2023 in Munich in hall A1.375 from November 14 to 17, 2023. For more information on the instrument, go to: https://www.rohde-schwarz.com/product/MXO5