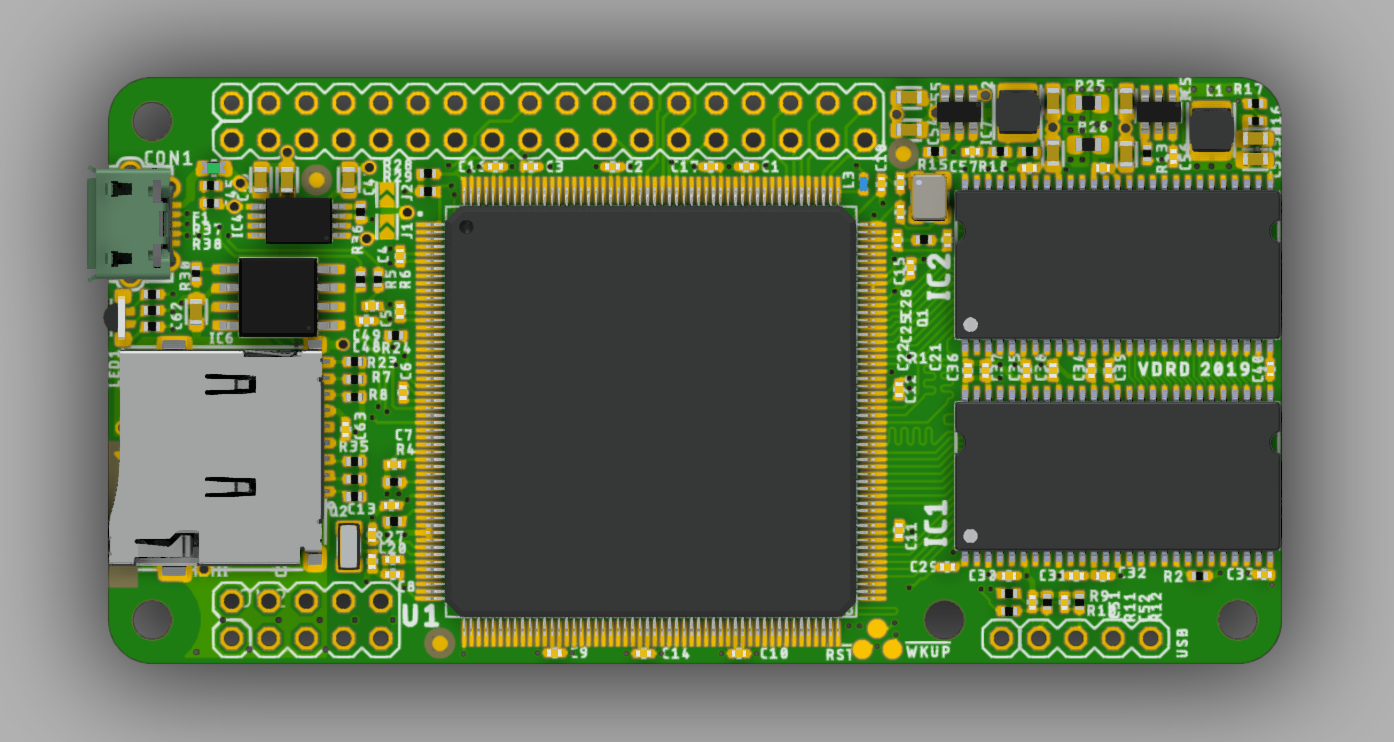
Hong Kong-based Amoeba Robotics is set to launch a pick and place machine for engineers, designers, and makers to conveniently automate the assembly of their PCBs ontop of their desks, with a more affordable price range going for $1,950. This is incredible because most pick and place machines are incredibly expensive, with the desktop models running into thousands of dollars or more.
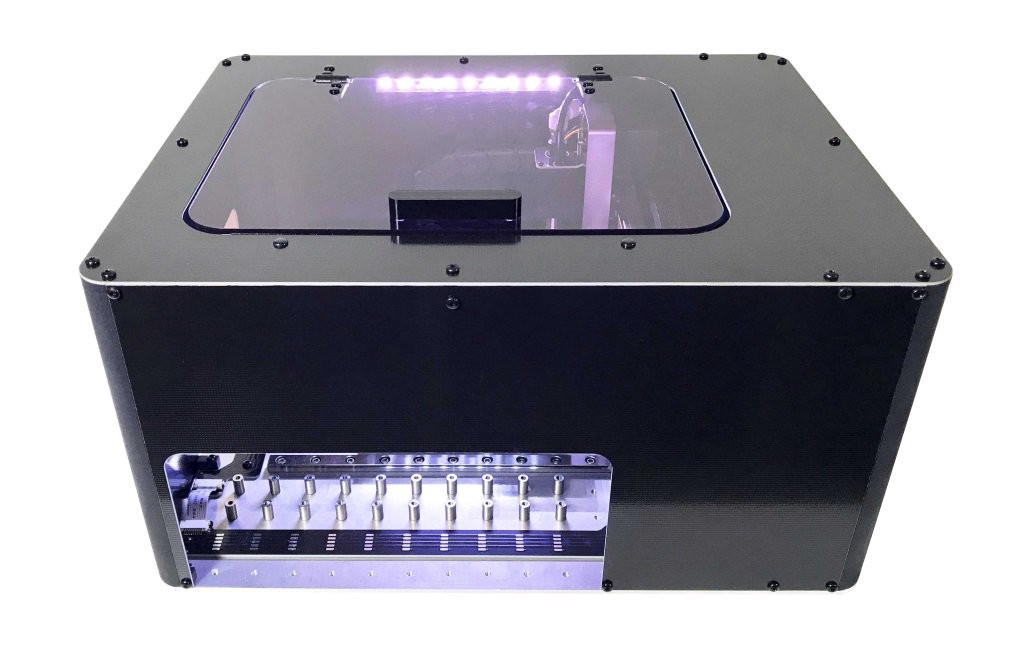
Founded in 2010, Amoeba Robotics is a Hong Kong-based research, engineering, and design company that focuses on advanced robotics and automation. The company says that their Boarditto is suitable for rapid prototyping and small-batch manufacturing, boasting of more than 15 components placed per minute. The device has an extensive feature set for a desktop machine and includes a dual camera setup, one above, and one below, which automatically detects fiducial markers that compensate for PCB misalignment, and corrects the position of each component during the pick and place process. Users have the option of up to 16 feeders loaded at any time and supports both JEDEC and custom trays.
The Boarditto doesn’t need a connection to the internet to function, this is due to its built-in computer (no specifics as to type), enabling you to add a monitor, keyboard, and mouse to program the machine using the Boarditto V1.0 app. “Amoeba” equipped the pick and place machine with a built-in vacuum pump to keep things neat, also has an automatic nozzle changer, and can accept PCBs at up to 160mm x 100mm.
Video
The Boarditto helps to free up your time and energy by leaving the repetitive task of assembling PCBs to a machine. It also helps in avoiding inaccuracies and mistakes that can easily occur when hand-soldering, such as bridging pins of fine-pitched components or placing a component on the wrong spot. Amoeba Robotics is currently accepting pre-orders for the Boarditto, and also some add-ons — including automatic tape feeders ($95), manual tape feeders ($20), aluminum tray holders ($190), and a soon-to-be-released “dittoReal,” which appears to be a giant part dispenser. If you pre-order before June 15, Amoeba will include a pair of auto-feeders and manual feeders free of charge.




![How to shrink your USB Type-C battery charger [PDF]](https://www.electronics-lab.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/MAX77860.png)