What is the working principle of a photovoltaic cell in solar power systems?
What is the working principle of a photovoltaic cell in solar power systems?
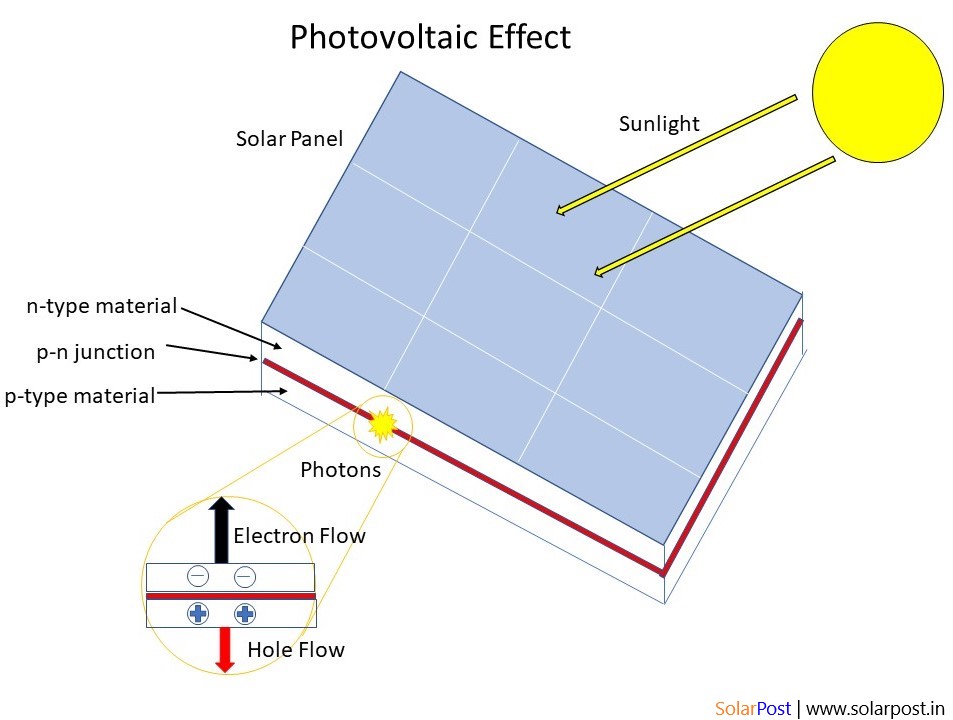
A photovoltaic (PV) cell, also known as a solar cell, is the basic building block of solar power systems. It is a device that converts sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
The working principle of a photovoltaic cell involves several key steps:
- Absorption of Sunlight: The photovoltaic cell is typically made of semiconductor material, such as silicon. When sunlight (which is composed of photons) strikes the cell, the photons with sufficient energy are absorbed by the semiconductor material.
- Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs: The absorbed photons transfer their energy to electrons in the semiconductor, causing them to be excited to a higher energy level. This creates “electron-hole” pairs, where the electron is excited to a higher energy state, leaving behind a positively charged “hole” in the lower energy state.
- Separation and Drift of Charge Carriers: The electric field within the semiconductor material separates the electron and the hole, preventing them from recombining immediately. The electrons are negatively charged and are free to move, while the holes are positively charged and also contribute to the overall current flow.
- Collection of Charge Carriers: The separated electrons and holes are collected by the semiconductor’s internal electrical contacts. Metal contacts are placed on the front and back surfaces of the cell to create an electrical pathway for the charge carriers.
- Flow of Current: When an external load is connected to the cell, the accumulated electrons flow through the external circuit, generating an electric current. This flow of electrons can be harnessed for various applications, such as powering electrical devices or charging batteries.
- Creation of Voltage: The flow of electrons through the external circuit creates a voltage difference or potential across the cell. This potential difference is known as the photovoltaic cell’s output voltage.
It’s important to note that a single photovoltaic cell typically produces a relatively low voltage and power output. To generate higher power levels, multiple cells are connected in series or parallel to form a solar module or panel. These modules can be further connected in arrays to create solar power systems capable of generating significant amounts of electricity.
Overall, the working principle of a photovoltaic cell relies on the ability of semiconductors to convert sunlight into electrical energy by exploiting the photovoltaic effect. This technology has become a crucial component of solar energy systems for generating clean and sustainable electricity.

