What is a SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) or thyristor?
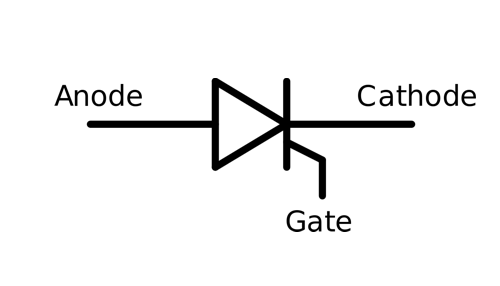
An SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier), also known as a thyristor, is a four-layer semiconductor device that acts as a controllable switch for high-power applications in both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) circuits. The SCR is widely used in electronic power control and conversion applications.
The SCR has three terminals: an anode (A), a cathode (K), and a gate (G). It is designed to allow current flow in one direction only, from the anode to the cathode. The gate terminal is used to control the conduction of current through the SCR.
The working principle of an SCR involves three main states:
- Forward Blocking State: In this state, the voltage across the SCR is below the minimum threshold voltage known as the forward breakover voltage (VBO). The SCR remains in a non-conducting state, and only a very small leakage current flows through it.
- Forward Conduction State: When the voltage across the SCR exceeds the forward breakover voltage (VBO) and a positive voltage pulse is applied to the gate terminal, the SCR enters the forward conduction state. In this state, the SCR becomes highly conductive, allowing a large current to flow from the anode to the cathode until the current falls below a certain holding current value.
- Reverse Blocking State: When the voltage across the SCR is reversed (negative), it enters the reverse blocking state. In this state, the SCR acts as an open circuit, blocking current flow in the reverse direction. It remains in the reverse blocking state until the voltage across it reaches a certain threshold value called the reverse breakover voltage (VR).
Once the SCR enters the forward conduction state, it continues to conduct even if the gate current is removed, until the current through it falls below the holding current. To turn off the SCR, the current through it must be reduced below the holding current or the applied voltage must be reversed.
SCRs are commonly used in applications that require high-power switching, such as motor control, heating systems, AC power control, and solid-state relays. They offer advantages such as high reliability, fast switching speed, and efficient power control, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and consumer electronic devices.

