What is the function of a transformer in power supply circuits?
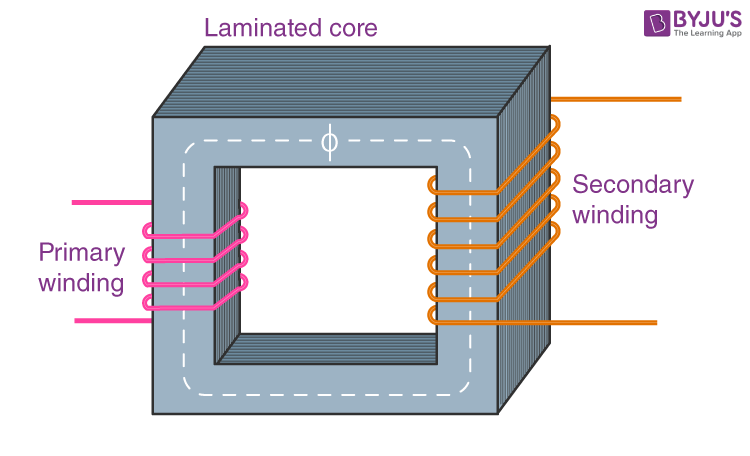
In power supply circuits, a transformer is an essential component that serves several functions. Here are the main functions of a transformer in a power supply circuit:
- Voltage Transformation: The primary function of a transformer is to change the voltage level of an AC (alternating current) signal. It can step up or step down the input voltage to the desired output voltage level. This voltage transformation is achieved by the ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings of the transformer.
- Isolation: Transformers provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits. The primary and secondary windings are electrically insulated from each other, which helps to prevent the transmission of high voltage or potentially dangerous voltage levels to the output side of the transformer.
- Impedance Matching: Transformers are also used for impedance matching between the power supply and the load. By selecting appropriate turns ratios, transformers can match the impedance of the load to the impedance of the power source, maximizing power transfer efficiency.
- Filtering and Regulation: In some power supply circuits, transformers are used in conjunction with rectifiers and capacitors to create a filtered DC output. The transformer provides the necessary AC voltage for the rectification process, and the subsequent filtering components smooth out the AC ripples, resulting in a stable DC output voltage.
- Galvanic Isolation: Transformers offer galvanic isolation, which means they prevent the flow of direct current (DC) between the input and output circuits. This feature is especially important in safety and noise reduction, as it helps to prevent ground loops, reduces the risk of electric shocks, and minimizes the transmission of electromagnetic interference (EMI) between circuits.
Overall, transformers play a crucial role in power supply circuits by facilitating voltage transformation, providing isolation, matching impedance, and aiding in the creation of stable DC outputs, ensuring the efficient and safe delivery of electrical power to various devices and systems.
mixos Edited answer 22 June, 2023
