What is the purpose of a capacitor in an electronic circuit?
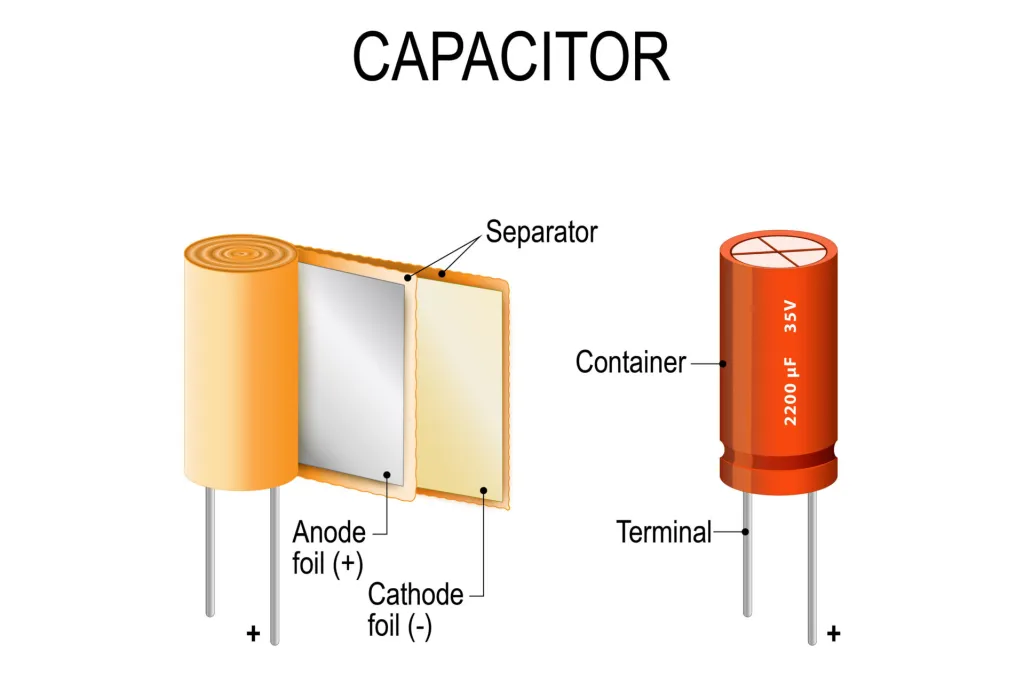
A capacitor is an essential component in electronic circuits and serves several important purposes:
- Energy Storage: One of the primary functions of a capacitor is to store electrical energy. When a voltage is applied across its terminals, the capacitor charges up by accumulating electric charge on its plates. This stored energy can be released when needed, providing a quick discharge of energy.
- Filtering and Smoothing: Capacitors are commonly used in power supply circuits to smooth out or filter voltage fluctuations. They can absorb and release electrical energy rapidly, helping to maintain a stable voltage level by reducing variations or “ripple” in the output.
- Timing and Delay: Capacitors, in conjunction with resistors, can be used to create timing circuits. By controlling the rate of charging and discharging of the capacitor, precise time delays can be achieved, enabling functions such as oscillation, pulse generation, or signal synchronization.
- Coupling and Decoupling: Capacitors are employed for coupling and decoupling signals in electronic circuits. In coupling, a capacitor allows the AC component of a signal to pass while blocking the DC component, enabling the transfer of the desired signal to another stage. In decoupling, capacitors are used to provide a low-impedance path for AC signals, bypassing noise or disturbances to the ground.
- Tuning and Filtering: Capacitors are extensively used in tuning circuits, such as radio frequency (RF) circuits, to select or adjust the resonance frequency. They can also be employed as part of filter circuits to allow or block specific frequencies, enabling the desired signals or removing unwanted noise.
- Motor Starters: In some applications, capacitors are utilized to provide an initial boost of power to start electric motors. These capacitors are called motor starters or motor run capacitors and help overcome the motor’s initial resistance and provide a phase shift to start rotation.
Overall, capacitors are versatile components that find applications in a wide range of electronic circuits, contributing to energy storage, signal processing, timing, and other critical functions.
mixos Edited answer 22 June, 2023

