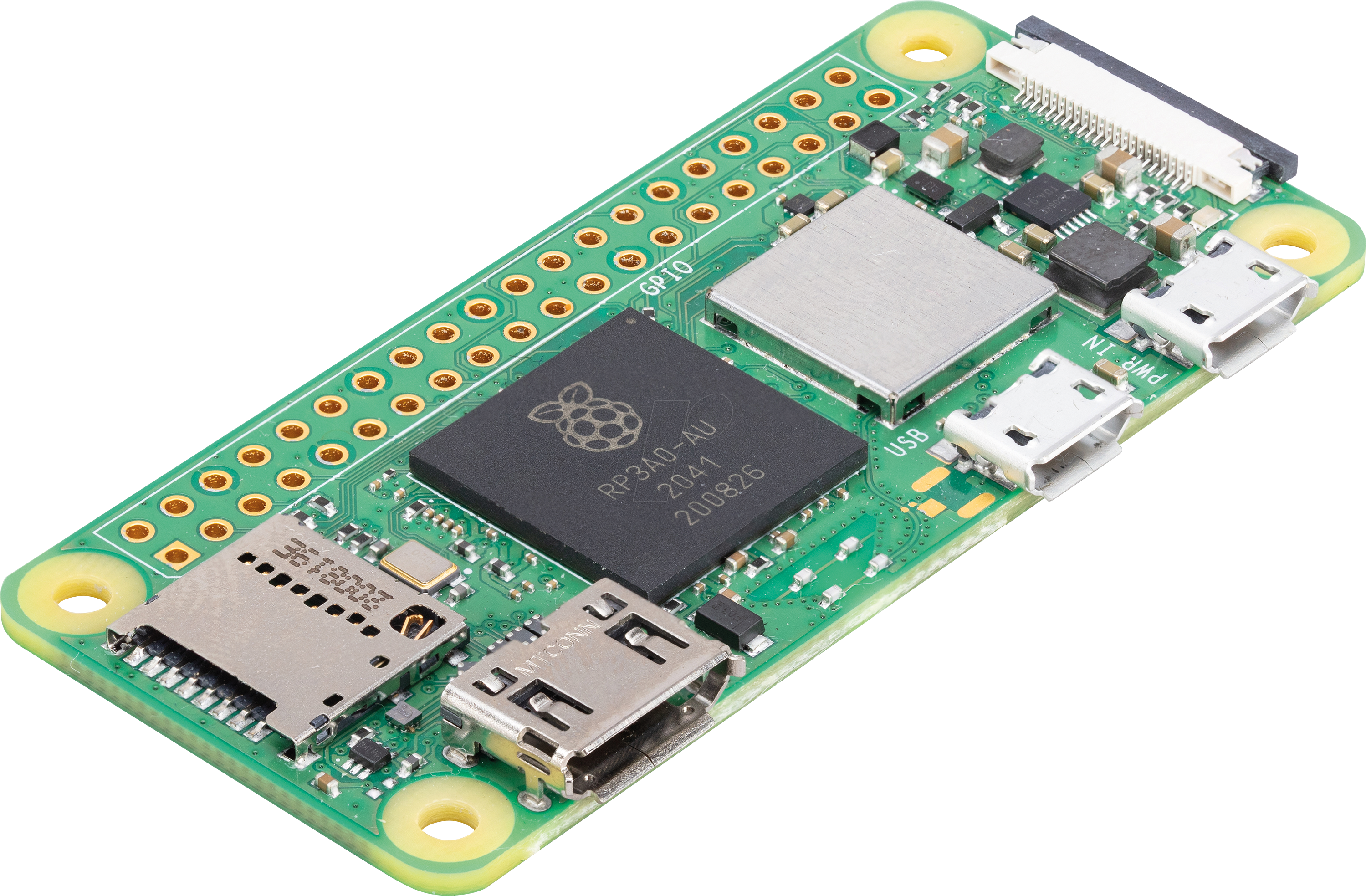
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W is a neat upgrade over Raspberry Pi Zero W. It comes in the same form factor of 65mm X 30mm, but it is 100% surface mount. Hence unlike Raspberry Pi Zero W, it sits flat.
Raspberry Pi Zero 2W comes with Broadcom BCM2710A1, 1Ghz quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 CPU core. Its quad-core CPU performance is 5x times faster than the single CPU performance of Raspberry Pi Zero W. Also, single-threaded process performance is 40 percent faster.
Additionally, the Pi Zero 2 W operating system is 3 times faster and boots the GUI in 30 seconds, as compared to 90 seconds for Zero W.
Other features of Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W are 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM, 2.4GHz IEEE 802.11b/g/n wireless LAN, Bluetooth 4.2, BLE for connectivity, 1 × USB 2.0 interface with OTG, HAT-compatible 40 pin I/O header footprint, MicroSD card slot, Mini HDMI port, Composite video and reset pin solder points, CSI-2 camera connector and OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0 graphics.
Now, getting into the details of how the performance of both the boards is evaluated, the exact performance uplift of Rpi Zero 2 W over Rpi Zero W varies across workloads but for multi-threaded sysbench it is five times faster.
What is Sysbench?
Sysbench is an open-source multi-threaded benchmark tool. It is based on the Lua JIT compiler. It can create arbitrarily complex workloads for comparative analysis. Sysbench provides utility for benchmarking databases, filesystems, CPUs, memory access, thread-based schedulers, mutex, etc. It generates reports with extensive statistics about rate and latency, including metrics like latency percentiles and histograms.
Support for native Windows build was removed in the sysbench 1.0 version. It could be reintroduced in future releases of the tool. Currently, the recommended method for obtaining sysbench on Windows is to use the Windows Subsystem for Linux, which is available in Windows 10.
Following the Debian/Ubuntu installation instructions after installing WSL and getting into the bash prompt on Windows is sufficient. Alternatively, WSL can be used to build and install sysbench from the source, or an older sysbench release can be used to generate a native binary.
To know more about sysbench, visit this link.
Summary
One of the USPs of this board is that its form factor and connectors match the original Rpi Zero W layout. Hence pre-existing use cases can easily swap in Zero 2W and get enhanced features and power without any major change.