Solid State Li-ion Batteries – High Energy-Dense Batteries Are Closer Than Before
The Interuniversity MicroElectronicss Centre (IMEC) is an independent research center which deals with nanoelectronics and digital technologies. Their headquarters are situated in Leuven, Belgium. Recently IMEC began to research and prototype Solid State Lithium-ion batteries. Solid State batteries are batteries which make use of solid electrodes and electrolytes. There have been a lot of research about Solid – State batteries, however, IMEC has moved from research to producing its first prototype.
Prototype Battery
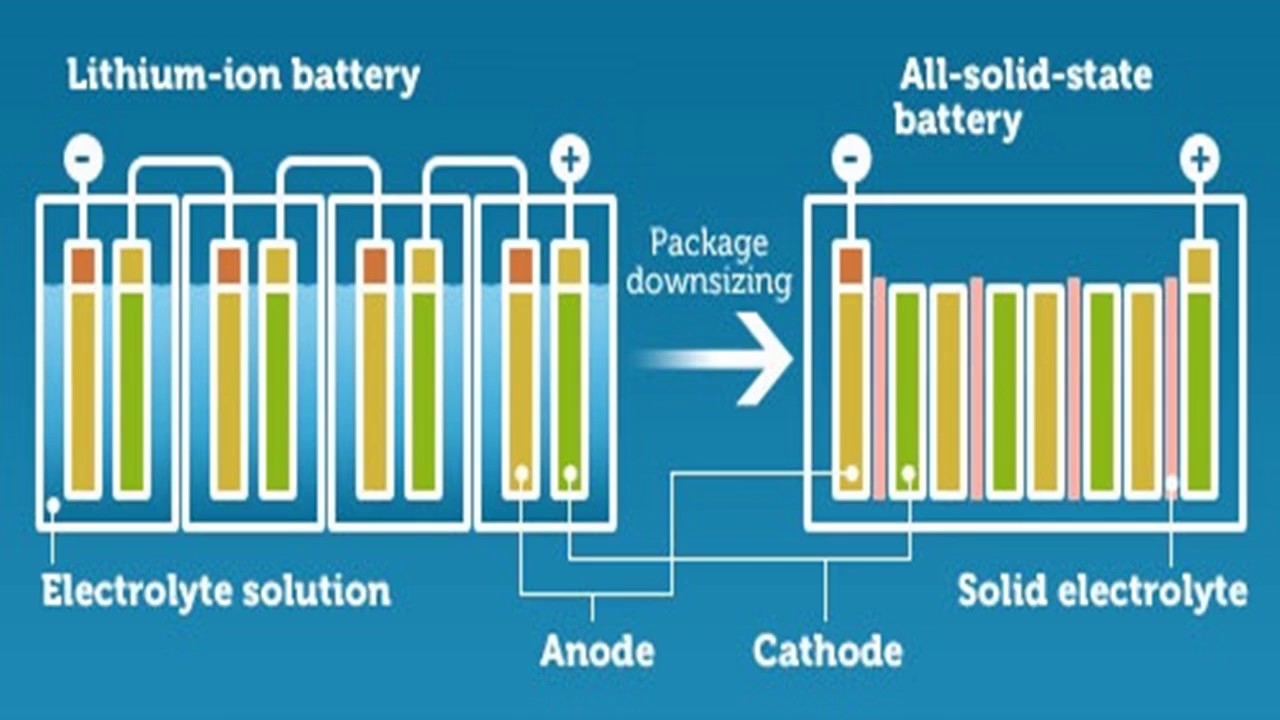
The battery produced has an energy density of two hundred Wh/L, can be charged within two hours and can accept a charge of 0.5 C. This was achieved through the use of Solid State electrolyte. Nanocomposite electrolyte with high conductivity features was used. The electrolyte starts out as a fluid before solidifying. Unlike liquid electrolyte-based batteries, batteries based on Solid State electrolytes have “inherent safe operating characteristics.” Here’s a scenario: Throwing a normal battery against the wall might cause it to burn due to the liquid electrolyte which is flammable, however Solid State Lithium-ion batteries don’t have anything to burn because lithium is not flammable in its solid state.
ADVANTAGES OF SOLID STATE ELECTROLYTES OVER FLUID ELECTROLYTES
A Solid State electrolyte has almost no degradation reaction left. Therefore it can last through ” hundreds of thousands of cycles.” Secondly, solid-state electrolytes are compatible with metal like lithium anodes thereby affording it the opportunity to obtain very high energy densities targets. This means that higher energy densities can be derived from Solid State electrolytes. Furthermore, fluid electrolytes based Lithium-ion batteries cannot perform well in extreme cold. Solid State electrolytes are capable of working under really low temperatures.
Another advantage is that the dense ceramic electrolyte prevents Li-dendrite shorting and overcomes thermal stability issues of currently used organic liquid electrolytes. The all-solid-state structure provides revolutionary dimensional tolerance and mechanical strength, decreasing packaging requirements and system weight.
Some of the potential applications of this will be :
- portable electronics (such as laptops or cameras).
- electric cars.
- home storage systems for the smart grid.
- future smart household appliances and autonomous robots.
MORE INFORMATION
IMEC hopes to achieve the development of a battery with an energy density of 1000Wh/L and charging time of 30 minutes (2C). The quest for solid-state batteries isn’t stopping with IMEC alone – MIT is in partnership with Samsung, and they have formed a team to work on Solid State batteries and electrolytes. The University of Maryland is also currently working on their own Solid State Lithium-ion battery. With the way things are going, it will not be long before liquid Lithium chemistry is completely replaced by Solid State electrolytes.