Tag: nanopower

Maxim Integrated MAX16161 nanoPower Supply Supervisor
Maxim Integrated MAX16161 nanoPower Supply Supervisor is an ultra-low current, single-channel supervisory IC with glitch-free power-up. The MAX16161 monitors the power supply voltage and asserts a reset when the input voltage falls below the reset threshold. After the monitoring...
Continue Reading
MAX16163/MAX16164 nanoPower On/Off Controller
Maxim's MAX16163 and MAX16164 nanoPower on/off controllers with programmable sleep time extend battery life up to 60% Maxim's MAX16163 and MAX16164 are nanoPower on/off controllers with programmable sleep time. The devices integrate a power switch to gate an output, which provides up...
Continue Reading
Glitch-Free Supervisor Delivers Robust Protection for Low-Voltage IoT Applications – MAX16162
Eliminate power-up errors with Maxim’s MAX16162 small, low-power, glitch-free supervisor Maxim’s MAX16162 ultra-low current, single-channel supervisory IC monitors the power supply voltage and asserts a reset when the input voltage falls below the reset threshold. After the...
Continue Reading
MAX17227A is a 2 A nanoPower boost converter
Maxim's MAX17227A is a 400 mV to 5.5 V input, 2 A nanoPower boost converter with short-circuit protection and True Shutdown™ Maxim's MAX17227A is a nanoPower boost converter, capable of delivering a load up to 2 A peak inductor current and providing True Shutdown,...
Continue Reading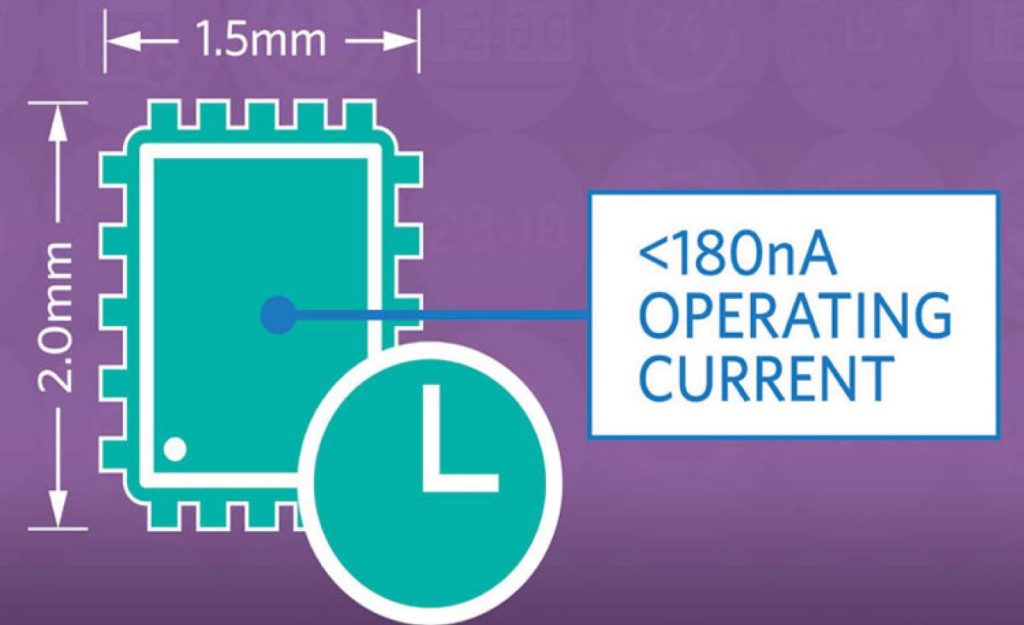
Real-time clock for wearables draws under 180nA
More than 35 percent smaller than the tiniest RTC alternatives, the MAX31341B nanoPower real-time clock (RTC) from Maxim Integrated Products operates at less than 180nA. By Julien Happich @ eenewsembedded.com The 2x1.5mm device offloads the central microcontroller from timekeeping,...
Continue Reading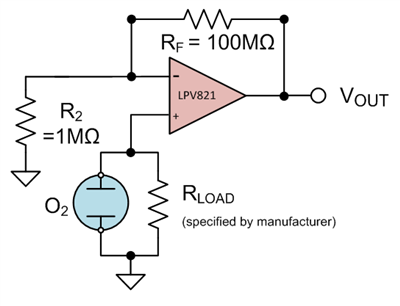
How to make precision measurements on a nanopower budget
Gen Vansteeg @ ti.com discuss about precision measurement for nanopower scale using OPAMPs. Heightened accuracy and speed in an operational amplifier (op amp) has a direct relationship with the magnitude of its power consumption. Decreasing the current consumption decreases the gain...
Continue Reading