Tohoku University Reveals Swallowable Thermometer at SemiCon Japan
A lot of people know that temperature is the degree of heat present in a substance. The common way of measuring body temperature is the armpit method where temperature is measured by putting the thermometer under the armpit. However, there are better ways of measuring this temperature. Right now, the most accurate temperature measure is the core or deep body temperature. Normally this method uses temperature gotten from the rectal area. Although it is accurate and efficient, it is not comfortable for most people.
Temperature is very important and valuable during research about “biological clocks; ovulation cycles, heat strokes, and even hypothermia.” Researchers from the Nakamura Lab at Tohoku University have created a swallowable thermometer which is the size of a tablet. The thermometer was unveiled at Semicon Japan 2018. It is similar to BodyCap’s e-Celsius Pill.
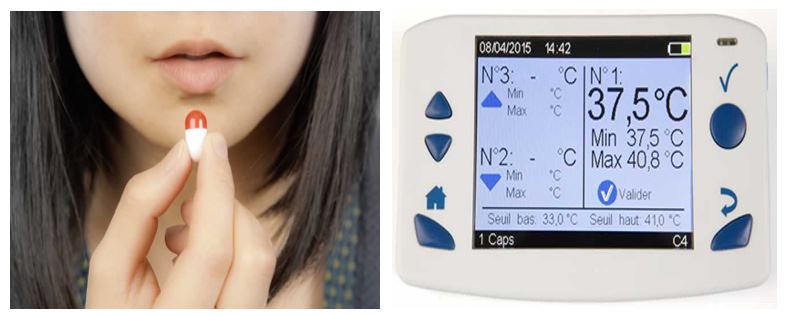
Back in 2017, BodyCap won the European CE Mark to release its “swallowable wireless thermometer” called e-Celsius. It has been designed to monitor patients’ core temperature, the e-Celsius Pill looks like a regular drug capsule. As it moves down the digestive tract, it transmits data wirelessly every 30 seconds to an “e-Viewer” that displays the readings and records the temperature during the pill’s journey. Tohoku’s Swallowable thermometer has been designed to do the same thing however; when compared to the e-Celsius pill, it is cheaper. Costs are expected to be less than a dollar while the e-Celsius will cost between $42 to $46.
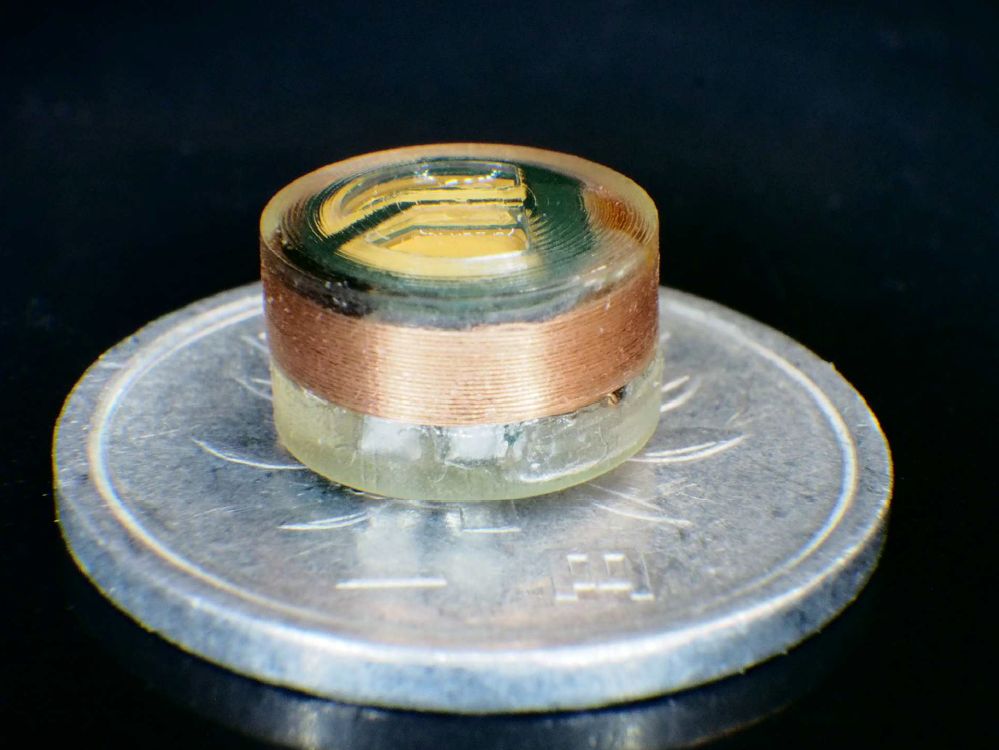
The thermometer has a diameter of 9.16mm and it works based on the Lemon Battery Principle; it uses magnesium and platinum electrodes to generate electricity because of the acidic environment of the human stomach. It has four components which are: a temperature sensor, a wireless communication chip, a customized chip that was produced using 0.6μm-process CMOS technology and a capacitor.
According to the University,
“it does not contain any substance that is harmful to the human body.”
Measurements are taken every 30 minutes to 60 minutes. It can work for almost 10 hours by storing energy generated while traveling within the body as electricity is stored in the capacitor. It uses the 10MHz frequency band for data, the frequency is not absorbed by the human body and is very efficient. The thermometer will improve what is known right now about temperature. The lab will soon be conducting tests at hospitals and athletic fields. [via]