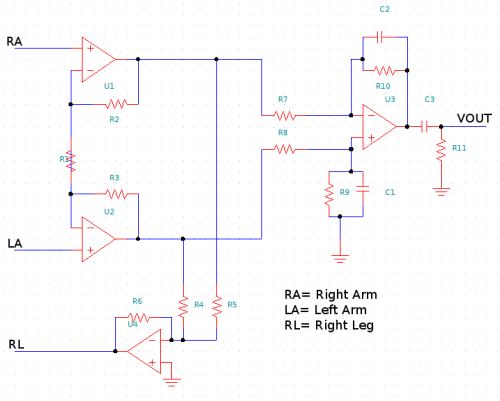
by Maurizio @ dev.emcelettronica.com:
Our body is built with biological tissue. The tissue that can generate or detect bioelectrical signals is called excitable tissue. Some examples of this tissue (and its cells) are: neurons and muscular tissue. Neurons are responsible of transmitting the excitatory bioelectrical signal to another neuron (forming nerves) or to a muscle tissue, gland or brain, while muscular cells are responsible of muscular contraction and distension. Some specialized cells generate bioelectric signals: optic receptors (eyes), muscular cells that transmit the feeling of pain, etc. Bioelectricity concerns the magnetic and electrical fields produced by organisms or cells.
Understanding bioelectricity – [Link]
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments